A novel role of the N terminus of budding yeast histone H3 variant Cse4 in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis
- PMID: 23525333
- PMCID: PMC3664860
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.113.149898
A novel role of the N terminus of budding yeast histone H3 variant Cse4 in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis
Abstract
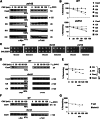
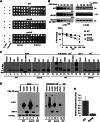
Regulating levels of centromeric histone H3 (CenH3) variant is crucial for genome stability. Interaction of Psh1, an E3 ligase, with the C terminus of Cse4 has been shown to contribute to its proteolysis. Here, we demonstrate a role for ubiquitination of the N terminus of Cse4 in regulating Cse4 proteolysis for faithful chromosome segregation and a role for Doa1 in ubiquitination of Cse4.
Keywords: Cse4; Doa1; Psh1; chromosome segregation; ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation.
Figures

References
-
- Black B. E., Jansen L. E., Maddox P. S., Foltz D. R., Desai A. B., et al. , 2007. Centromere identity maintained by nucleosomes assembled with histone H3 containing the CENP-A targeting domain. Mol. Cell 25: 309–322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

