Inhibition of the Rho signaling pathway improves neurite outgrowth and neuronal differentiation of mouse neural stem cells
- PMID: 23525456
- PMCID: PMC3601458
Inhibition of the Rho signaling pathway improves neurite outgrowth and neuronal differentiation of mouse neural stem cells
Abstract
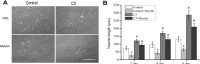
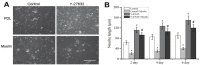
Neurons in the adult mammalian CNS do not spontaneously regenerate axons after injury due to CNS myelin and other inhibitory factors. Previous studies have showed that inhibition of the Rho-ROCK pathway promotes axonal outgrowth in primary neurons or in spinal cord injury models. Furthermore, RhoA inhibitor C3 transferase has a potential effect to induce neural differentiation in primary cultured neurons and cell lines. As stem cells and stem cell-derived neural progenitor cells have emerged as a regenerative medicine for stroke, Parkinson's disease and other neurological disorders, strategies that can promote axonal outgrowth and neuronal differentiation appear to have promising benefits in the cell-based therapy. Currently, how changes in the Rho-ROCK pathway may affect the neurite outgrowth and neuronal differentiation of stem cells has been poorly understood. The present investigation examined the effects of RhoA inhibition on neurite outgrowth and neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells (NSCs) isolated from the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the mouse. Our results show that inhibition of RhoA leads to neurite outgrowth of NSCs not only on normal culture substrate, poly-D-lysine (PDL), but also on myelin substrate. Moreover, inhibition of RhoA improves neuronal differentiation of NSCs and up-regulates biomarkers of neuronal gene expression. These results support that the Rho signaling pathway plays an important role in neurite development and neuronal differentiation of NSCs.
Keywords: Neural stem cells; Rho signaling pathway; myelin; neurite outgrowth; neuronal differentiation.
Figures
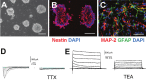
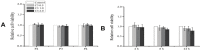
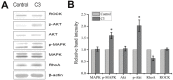
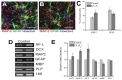

References
-
- Gage FH. Mammalian neural stem cells. Science. 2000;287:1433–1438. - PubMed
-
- Song HJ, Stevens CF, Gage FH. Neural stem cells from adult hippocampus develop essential properties of functional CNS neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:438–445. - PubMed
-
- Taupin P. Adult neural stem cells, neurogenic niches, and cellular therapy. Stem Cell Rev. 2006;2:213–219. - PubMed
-
- Bithell A, Williams BP. Neural stem cells and cell replacement therapy: making the right cells. Clin Sci (Lond) 2005;108:13–22. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
