Barriers to effective treatment of vaginal atrophy with local estrogen therapy
- PMID: 23525842
- PMCID: PMC3603331
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S43192
Barriers to effective treatment of vaginal atrophy with local estrogen therapy
Abstract
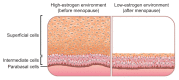
Vaginal atrophy is a common condition among postmenopausal women, among whom many exhibit both vulvovaginal symptoms (eg, dryness, irritation, itching, and pain with intercourse) and urinary symptoms (eg, increased frequency, urgency, incontinence, urinary tract infections, and dysuria). Unfortunately, few women with symptoms of vaginal atrophy report seeking treatment from a health care provider. The goal of this article is to examine reasons why patients and health care providers do not engage in discourse regarding this important topic. It is important to initiate conversations with postmenopausal women and counsel them on both why the changes occur and potential treatment options.
Keywords: barriers; local estrogen therapy; postmenopausal women; vaginal atrophy.
Figures
References
-
- Santoro N, Komi J. Prevalence and impact of vaginal symptoms among postmenopausal women. J Sex Med. 2009;6(8):2133–2142. - PubMed
-
- Nappi RE, Kokot-Kierepa M. Women’s voices in the menopause: results from an international survey on vaginal atrophy. Maturitas. 2010;67(3):233–238. - PubMed
-
- The North American Menopause Society. The role of local vaginal estrogen for treatment of vaginal atrophy in postmenopausal women: 2007 position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2007;14(3):357–369. - PubMed
-
- Sturdee DW, Panay N on behalf of the International Menopause Society Writing Group. Recommendations for the management of postmenopausal vaginal atrophy. Climacteric. 2010;13(6):509–522. - PubMed
-
- Stika CS. Atrophic vaginitis. Dermatol Ther. 2010;23(5):514–522. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

