Small is fast: astrocytic glucose and lactate metabolism at cellular resolution
- PMID: 23526722
- PMCID: PMC3605549
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00027
Small is fast: astrocytic glucose and lactate metabolism at cellular resolution
Abstract
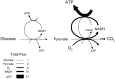
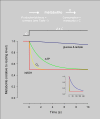
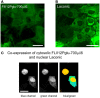
Brain tissue is highly dynamic in terms of electrical activity and energy demand. Relevant energy metabolites have turnover times ranging from milliseconds to seconds and are rapidly exchanged between cells and within cells. Until recently these fast metabolic events were inaccessible, because standard isotopic techniques require use of populations of cells and/or involve integration times of tens of minutes. Thanks to fluorescent probes and recently available genetically-encoded optical nanosensors, this Technology Report shows how it is now possible to monitor the concentration of metabolites in real-time and in single cells. In combination with ad hoc inhibitor-stop protocols, these probes have revealed a key role for K(+) in the acute stimulation of astrocytic glycolysis by synaptic activity. They have also permitted detection of the Warburg effect in single cancer cells. Genetically-encoded nanosensors currently exist for glucose, lactate, NADH and ATP, and it is envisaged that other metabolite nanosensors will soon be available. These optical tools together with improved expression systems and in vivo imaging, herald an exciting era of single-cell metabolic analysis.
Keywords: FLII12Pglu-700δμ6; FRET; cancer metabolism; flux; glycolysis; laconic; mitochondria.
Figures


References
-
- Barros L. F., Baeza-Lehnert F., Valdebenito R., Ceballo S., Alegría K. (2013). Fluorescent nanosensor based flux analysis: overview and the example of glucose, in Springer Protocols: Brain Energy Metabolism, eds Waagepetersen H. S., Hirrlinger J. (New York, NY: Springer; ), (in press).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

