Laurdan fluorescence lifetime discriminates cholesterol content from changes in fluidity in living cell membranes
- PMID: 23528083
- PMCID: PMC3602759
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.12.057
Laurdan fluorescence lifetime discriminates cholesterol content from changes in fluidity in living cell membranes
Abstract
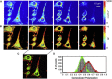
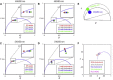
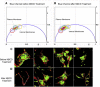
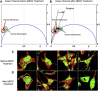
Detection of the fluorescent properties of Laurdan has been proven to be an efficient tool to investigate membrane packing and ordered lipid phases in model membranes and living cells. Traditionally the spectral shift of Laurdan's emission from blue in the ordered lipid phase of the membrane (more rigid) toward green in the disordered lipid phase (more fluid) is quantified by the generalized polarization function. Here, we investigate the fluorescence lifetime of Laurdan at two different emission wavelengths and find that when the dipolar relaxation of Laurdan's emission is spectrally isolated, analysis of the fluorescence decay can distinguish changes in membrane fluidity from changes in cholesterol content. Using the phasor representation to analyze changes in Laurdan's fluorescence lifetime we obtain two different phasor trajectories for changes in polarity versus changes in cholesterol content. This gives us the ability to resolve in vivo membranes with different properties such as water content and cholesterol content and thus perform a more comprehensive analysis of cell membrane heterogeneity. We demonstrate this analysis in NIH3T3 cells using Laurdan as a biosensor to monitor changes in the membrane water content during cell migration.
Copyright © 2013 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disorder Amidst Membrane Order: Standardizing Laurdan Generalized Polarization and Membrane Fluidity Terms.J Fluoresc. 2017 Jan;27(1):243-249. doi: 10.1007/s10895-016-1951-8. Epub 2016 Oct 13. J Fluoresc. 2017. PMID: 27738919 Review.
-
LAURDAN since Weber: The Quest for Visualizing Membrane Heterogeneity.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Feb 16;54(4):976-987. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00687. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 33513300 Free PMC article.
-
LAURDAN fluorescence and phasor plots reveal the effects of a H2O2 bolus in NIH-3T3 fibroblast membranes dynamics and hydration.Free Radic Biol Med. 2018 Nov 20;128:144-156. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.06.004. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 29885356 Free PMC article.
-
Laurdan monitors different lipids content in eukaryotic membrane during embryonic neural development.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014 Nov;70(2):785-94. doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-9982-8. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014. PMID: 24839062 Free PMC article.
-
Laurdan studies of membrane lipid-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor protein interactions.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;400:531-42. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-519-0_36. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17951758 Review.
Cited by
-
Disorder Amidst Membrane Order: Standardizing Laurdan Generalized Polarization and Membrane Fluidity Terms.J Fluoresc. 2017 Jan;27(1):243-249. doi: 10.1007/s10895-016-1951-8. Epub 2016 Oct 13. J Fluoresc. 2017. PMID: 27738919 Review.
-
Investigation of the Membrane Fluidity Regulation of Fatty Acid Intracellular Distribution by Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging of Novel Polarity Sensitive Fluorescent Derivatives.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 18;22(6):3106. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063106. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33803648 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxamido steroids inhibit the opening properties of transient receptor potential ion channels by lipid raft modulation.J Lipid Res. 2018 Oct;59(10):1851-1863. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M084723. Epub 2018 Aug 9. J Lipid Res. 2018. PMID: 30093524 Free PMC article.
-
Time-Resolved Laurdan Fluorescence Reveals Insights into Membrane Viscosity and Hydration Levels.Biophys J. 2018 Oct 16;115(8):1498-1508. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.08.041. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 30269886 Free PMC article.
-
Spectral Relaxation Imaging Microscopy II: Complex Dynamics.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 31;24(15):12271. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512271. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Edidin M. Lipids on the frontier: a century of cell-membrane bilayers. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003;4:414–418. - PubMed
-
- Pietzsch, J. 2004. Mind the membrane. Horizon Symposia: Living Frontier: 1–4.
-
- Helmreich E.J. Environmental influences on signal transduction through membranes: a retrospective mini-review. Biophys. Chem. 2003;100:519–534. - PubMed
-
- Sok M., Sentjurc M., Rott T. Cell membrane fluidity and prognosis of lung cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2002;73:1567–1571. - PubMed
-
- Chauhan N.B. Membrane dynamics, cholesterol homeostasis, and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Lipid Res. 2003;44:2019–2029. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

