Fatty acid-regulated transcription factors in the liver
- PMID: 23528177
- PMCID: PMC3940310
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-071812-161139
Fatty acid-regulated transcription factors in the liver
Abstract
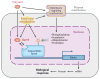
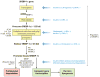
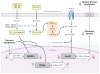
Fatty acid regulation of hepatic gene transcription was first reported in the early 1990s. Several transcription factors have been identified as targets of fatty acid regulation. This regulation is achieved by direct fatty acid binding to the transcription factor or by indirect mechanisms where fatty acids regulate signaling pathways controlling the expression of transcription factors or the phosphorylation, ubiquitination, or proteolytic cleavage of the transcription factor. Although dietary fatty acids are well-established regulators of hepatic transcription factors, emerging evidence indicates that endogenously generated fatty acids are equally important in controlling transcription factors in the context of glucose and lipid homeostasis. Our first goal in this review is to provide an up-to-date examination of the molecular and metabolic bases of fatty acid regulation of key transcription factors controlling hepatic metabolism. Our second goal is to link these mechanisms to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a growing health concern in the obese population.
Figures

References
-
- Adams CM, Reitz J, De Brabander JK, Feramisco JD, Li L, et al. Cholesterol and 25-hydroxycholesterol inhibit activation of SREBPs by different mechanisms, both involving SCAP and Insigs. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:52772–80. - PubMed
-
- Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J. The metabolic syndrome—a new worldwide definition. Lancet. 2005;366:1059–62. - PubMed
-
- Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1221–31. - PubMed
-
- Arnold C, Konkel A, Fischer R, Schunck W-H. Cytochrome P450-dependent metabolism of omega-6 and omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Pharmacol Rep. 2010;62:536–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

