Recurrent upper limb ischaemia due to a crutch-induced brachial artery aneurysm
- PMID: 23529749
- PMCID: PMC3686390
- DOI: 10.1093/icvts/ivt121
Recurrent upper limb ischaemia due to a crutch-induced brachial artery aneurysm
Abstract
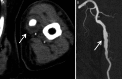
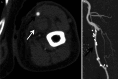
An 83-year old man who had used bilateral axillary crutches for 67 years was referred to our hospital for acute left upper limb ischaemia. He underwent successful recanalization through emergent catheter thromboembolectomy. However, a crutch-induced left brachial artery aneurysm was subsequently detected by computed tomography. Therefore, we performed aneurysm exclusion and subsequent saphenous vein bypass grafting. When a crutch user presents with upper limb ischaemia, a high index of suspicion and early identification of the crutch induced vascular injury are mandatory for appropriate treatment.
Keywords: Brachial artery aneurysm; Crutch-induced vascular injury; Upper limb ischaemia.
Figures
References
-
- Earnshaw JJ. Acute ischemia: evaluation and decision making. In: Cronenwett JL, Johnston KW, editors. Rutherford's Vascular Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier; 2010. pp. 2389–98.
-
- Feldman DR, Vujic I, McKay D, Callcott F, Uflacker R. Crutch-induced axillary artery injury. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1995;18:296–9. - PubMed
-
- Moon IS, Hwang JK, Kim JI. Recurrent upper extremity embolism due to a crutch-induced arterial injury: a different cause of upper extremity embolism. Ann Vasc Surg. 2010;24:554.e7–12.e7. doi:10.1016/j.avsg.2009.11.005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical