The thymic medulla is required for Foxp3+ regulatory but not conventional CD4+ thymocyte development
- PMID: 23530124
- PMCID: PMC3620359
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20122070
The thymic medulla is required for Foxp3+ regulatory but not conventional CD4+ thymocyte development
Abstract
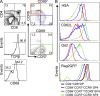
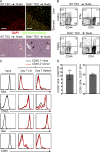
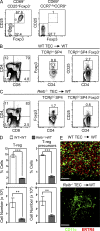
A key role of the thymic medulla is to negatively select autoreactive CD4(+) and CD8(+) thymocytes, a process important for T cell tolerance induction. However, the involvement of the thymic medulla in other aspects of αβ T cell development, including the generation of Foxp3(+) natural regulatory T cells (nTreg cells) and the continued maturation of positively selected conventional αβ T cells, is unclear. We show that newly generated conventional CD69(+)Qa2(-) CD4 single-positive thymocytes mature to the late CD69(-)Qa2(+) stage in the absence of RelB-dependent medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs). Furthermore, an increasing ability to continue maturation extrathymically is observed within the CD69(+)CCR7(-/lo)CCR9(+) subset of conventional SP4 thymocytes, providing evidence for an independence from medullary support by the earliest stages after positive selection. In contrast, Foxp3(+) nTreg cell development is medullary dependent, with mTECs fostering the generation of Foxp3(-)CD25(+) nTreg cell precursors at the CD69(+)CCR7(+)CCR9(-) stage. Our results demonstrate a differential requirement for the thymic medulla in relation to CD4 conventional and Foxp3(+) thymocyte lineages, in which an intact mTEC compartment is a prerequisite for Foxp3(+) nTreg cell development through the generation of Foxp3(-)CD25(+) nTreg cell precursors.
Figures


Comment in
-
Regulatory T cells: the thymic medulla - a cradle for TReg cell development.Nat Rev Immunol. 2013 May;13(5):304. doi: 10.1038/nri3453. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23598649 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

