Insight into the assembly mechanism in the supramolecular rings of the sodium-driven Vibrio flagellar motor from the structure of FlgT
- PMID: 23530206
- PMCID: PMC3625306
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1222655110
Insight into the assembly mechanism in the supramolecular rings of the sodium-driven Vibrio flagellar motor from the structure of FlgT
Abstract
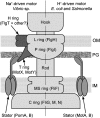
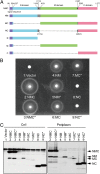
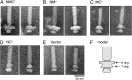
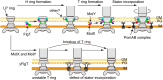
Flagellar motility is a key factor for bacterial survival and growth in fluctuating environments. The polar flagellum of a marine bacterium, Vibrio alginolyticus, is driven by sodium ion influx and rotates approximately six times faster than the proton-driven motor of Escherichia coli. The basal body of the sodium motor has two unique ring structures, the T ring and the H ring. These structures are essential for proper assembly of the stator unit into the basal body and to stabilize the motor. FlgT, which is a flagellar protein specific for Vibrio sp., is required to form and stabilize both ring structures. Here, we report the crystal structure of FlgT at 2.0-Å resolution. FlgT is composed of three domains, the N-terminal domain (FlgT-N), the middle domain (FlgT-M), and the C-terminal domain (FlgT-C). FlgT-M is similar to the N-terminal domain of TolB, and FlgT-C resembles the N-terminal domain of FliI and the α/β subunits of F1-ATPase. To elucidate the role of each domain, we prepared domain deletion mutants of FlgT and analyzed their effects on the basal-body ring formation. The results suggest that FlgT-N contributes to the construction of the H-ring structure, and FlgT-M mediates the T-ring association on the LP ring. FlgT-C is not essential but stabilizes the H-ring structure. On the basis of these results, we propose an assembly mechanism for the basal-body rings and the stator units of the sodium-driven flagellar motor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
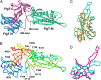

Similar articles
-
In Situ Structure of the Vibrio Polar Flagellum Reveals a Distinct Outer Membrane Complex and Its Specific Interaction with the Stator.J Bacteriol. 2020 Jan 29;202(4):e00592-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00592-19. Print 2020 Jan 29. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 31767780 Free PMC article.
-
The flagellar basal body-associated protein FlgT is essential for a novel ring structure in the sodium-driven Vibrio motor.J Bacteriol. 2010 Nov;192(21):5609-15. doi: 10.1128/JB.00720-10. Epub 2010 Aug 20. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20729351 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the stator assembly of the Vibrio flagellar motor from the crystal structure of MotY.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jun 3;105(22):7696-701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0800308105. Epub 2008 May 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18505842 Free PMC article.
-
The bacterial flagellar motor and its structural diversity.Trends Microbiol. 2015 May;23(5):267-74. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2014.12.011. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Trends Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25613993 Review.
-
Structure and Energy-Conversion Mechanism of the Bacterial Na+-Driven Flagellar Motor.Trends Microbiol. 2020 Sep;28(9):719-731. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.03.010. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Trends Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32781026 Review.
Cited by
-
Oligomeric lipoprotein PelC guides Pel polysaccharide export across the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 14;114(11):2892-2897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1613606114. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28242707 Free PMC article.
-
The Vibrio H-Ring Facilitates the Outer Membrane Penetration of the Polar Sheathed Flagellum.J Bacteriol. 2018 Oct 10;200(21):e00387-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00387-18. Print 2018 Nov 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 30104237 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, Assembly, and Function of Tripartite Efflux and Type 1 Secretion Systems in Gram-Negative Bacteria.Chem Rev. 2021 May 12;121(9):5479-5596. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00055. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Chem Rev. 2021. PMID: 33909410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Situ Structure of the Vibrio Polar Flagellum Reveals a Distinct Outer Membrane Complex and Its Specific Interaction with the Stator.J Bacteriol. 2020 Jan 29;202(4):e00592-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00592-19. Print 2020 Jan 29. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 31767780 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, gene regulation and environmental response of flagella in Vibrio.Front Microbiol. 2013 Dec 25;4:410. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00410. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24400002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berg HC. The rotary motor of bacterial flagella. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:19–54. - PubMed
-
- Terashima H, Kojima S, Homma M. Flagellar motility in bacteria structure and function of flagellar motor. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2008;270:39–85. - PubMed
-
- Minamino T, Imada K, Namba K. Molecular motors of the bacterial flagella. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008;18(6):693–701. - PubMed
-
- Kojima S, Blair DF. The bacterial flagellar motor: Structure and function of a complex molecular machine. Int Rev Cytol. 2004;233:93–134. - PubMed
-
- Yorimitsu T, Homma M. Na+-driven flagellar motor of Vibrio. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1505(1):82–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

