Neurotransmitters and synaptic components in the Merkel cell-neurite complex, a gentle-touch receptor
- PMID: 23530998
- PMCID: PMC3638015
- DOI: 10.1111/nyas.12057
Neurotransmitters and synaptic components in the Merkel cell-neurite complex, a gentle-touch receptor
Abstract
Merkel cells are an enigmatic group of rare cells found in the skin of vertebrates. Most make contacts with somatosensory afferents to form Merkel cell-neurite complexes, which are gentle-touch receptors that initiate slowly adapting type I responses. The function of Merkel cells within the complex remains debated despite decades of research. Numerous anatomical studies demonstrate that Merkel cells form synaptic-like contacts with sensory afferent terminals. Moreover, recent molecular analysis reveals that Merkel cells express dozens of presynaptic molecules that are essential for synaptic vesicle release in neurons. Merkel cells also produce a host of neuroactive substances that can act as fast excitatory neurotransmitters or neuromodulators. Here, we review the major neurotransmitters found in Merkel cells and discuss these findings in relation to the potential function of Merkel cells in touch reception.
© 2013 New York Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
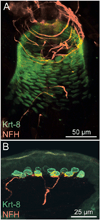

References
-
- Gardner EP, Martin JH, Jessell TM. In: Principles of Neuroscience. Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, editors. Oxford University Press; 2000. pp. 430–449.
-
- Rice FL, Albrecht PJ. In: The Senses: A Comprehensive Reference. Basbaum Allan I, et al., editors. Academic Press; 2008. pp. 1–31.
-
- Lumpkin EA, Caterina MJ. Mechanisms of sensory transduction in the skin. Nature. 2007;445:858–865. - PubMed
-
- Olausson H, Wessberg J, Morrison I, McGlone F, Vallbo A. The neurophysiology of unmyelinated tactile afferents. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2010;34:185–191. Epub 2008 Oct 2008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

