Natural killer cell inhibitory receptor expression in humans and mice: a closer look
- PMID: 23532016
- PMCID: PMC3607804
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00065
Natural killer cell inhibitory receptor expression in humans and mice: a closer look
Abstract
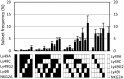
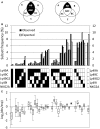
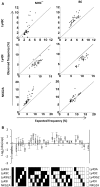
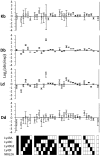
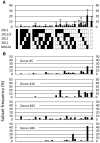
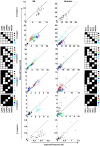
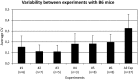
The Natural Killer (NK) cell population is composed of subsets of varying sizes expressing different combinations of inhibitory receptors for MHC class I molecules. Genes within the NK gene complex, including the inhibitory receptors themselves, seem to be the primary intrinsic regulators of inhibitory receptor expression, but the MHC class I background is an additional Modulating factor. In this paper, we have performed a parallel study of the inhibitory receptor repertoire in inbred mice of the C57Bl/6 background and in a cohort of 44 humans. Deviations of subset frequencies from the "product rule (PR)," i.e., differences between observed and expected frequencies of NK cells, were used to identify MHC-independent and MHC-dependent control of receptor expression frequencies. Some deviations from the PR were similar in mice and humans, such as the decreased presence of NK cell subset lacking inhibitory receptors. Others were different, including a role for NKG2A in determining over- or under-representation of specific subsets in humans but not in mice. Thus, while human and murine inhibitory receptor repertoires differed in details, there may also be shared principles governing NK cell repertoire formation in these two species.
Keywords: Ly49; MHC class I; killer immunoglobulin-like receptor; product rule; repertoire.
Figures
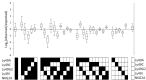
References
-
- Achour A., Persson K., Harris R. A., Sundback J., Sentman C. L., Lindqvist Y., et al. (1998). The crystal structure of H-2Dd MHC class I complexed with the HIV-1-derived peptide P18-I10 at 2.4 A resolution: implications for T cell and NK cell recognition. Immunity 9, 199–20810.1016/S1074-7613(00)80602-0 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

