HIRREM™: a noninvasive, allostatic methodology for relaxation and auto-calibration of neural oscillations
- PMID: 23532171
- PMCID: PMC3607159
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.116
HIRREM™: a noninvasive, allostatic methodology for relaxation and auto-calibration of neural oscillations
Abstract
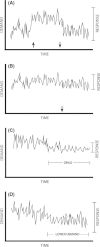
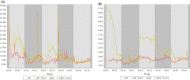
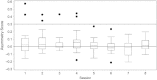
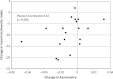
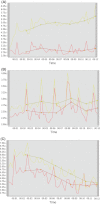
Disturbances of neural oscillation patterns have been reported with many disease states. We introduce methodology for HIRREM™ (high-resolution, relational, resonance-based electroencephalic mirroring), also known as Brainwave Optimization™, a noninvasive technology to facilitate relaxation and auto-calibration of neural oscillations. HIRREM is a precision-guided technology for allostatic therapeutics, intended to help the brain calibrate its own functional set points to optimize fitness. HIRREM technology collects electroencephalic data through two-channel recordings and delivers a series of audible musical tones in near real time. Choices of tone pitch and timing are made by mathematical algorithms, principally informed by the dominant frequency in successive instants of time, to permit resonance between neural oscillatory frequencies and the musical tones. Relaxation of neural oscillations through HIRREM appears to permit auto-calibration toward greater hemispheric symmetry and more optimized proportionation of regional spectral power. To illustrate an application of HIRREM, we present data from a randomized clinical trial of HIRREM as an intervention for insomnia (n = 19). On average, there was reduction of right-dominant temporal lobe high-frequency (23-36 Hz) EEG asymmetry over the course of eight successive HIRREM sessions. There was a trend for correlation between reduction of right temporal lobe dominance and magnitude of insomnia symptom reduction. Disturbances of neural oscillation have implications for both neuropsychiatric health and downstream peripheral (somatic) physiology. The possibility of noninvasive optimization for neural oscillatory set points through HIRREM suggests potentially multitudinous roles for this technology. Research is currently ongoing to further explore its potential applications and mechanisms of action.
Keywords: Allostasis; HIRREM; auto-calibration; biofeedback; electroencephalography; hemispheric asymmetry; insomnia; neural oscillation; relaxation; stochastic resonance.
Figures
References
-
- Angelakis E, Lubar JF, Stathopoulou S, Kounios J. Peak alpha frequency: an electroencephalographic measure of cognitive preparedness. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004;115:887–897. - PubMed
-
- Anokhin AP, Lutzenberger W, Nikolaev A, Birmbaumer N. Complexity of electrocortical dynamics in children: developmental aspects. Dev. Psychobiol. 2000;36:9–22. - PubMed
-
- Arns M, Strehl S, de Ridder U, Breteler M, Coenen A. Efficacy of neurofeedback treatment in ADHD: the effects on inattention, impulsivity and hyperactivity: a meta-analysis. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2009;40:180–189. - PubMed
-
- Avnon Y, Nitzan M, Sprecher E, Rogowski Z, Yarnitsky D. Autonomic asymmetry in migraine: augmented parasympathetic activation in left unilateral migraineurs. Brain. 2004;127:2099–2108. - PubMed
-
- Babiloni C, Visser PJ, Frisoni G, Bresciani PP, De Deyn L, Jelic V, et al. Cortical sources of resting EEG rhythms in mild cognitive impairment and subjective memory complaint. Neurobiol. Aging. 2010;31:1787–1798. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

