PUMA and BIM are required for oncogene inactivation-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 23532334
- PMCID: PMC3753585
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.2003483
PUMA and BIM are required for oncogene inactivation-induced apoptosis
Abstract
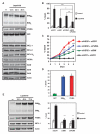
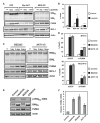
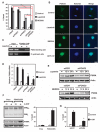
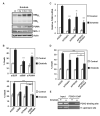
The clinical efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors supports the dependence of distinct subsets of cancers on specific driver mutations for survival, a phenomenon called "oncogene addiction." We demonstrate that PUMA and BIM are the key apoptotic effectors of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in breast cancers with amplification of the gene encoding human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) and lung cancers with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutants. The BH3 domain containing proteins BIM and PUMA can directly activate the proapoptotic proteins BAX and BAK to permeabilize mitochondria, leading to caspase activation and apoptosis. We delineated the signal transduction pathways leading to the induction of BIM and PUMA by tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Inhibition of the mitogen-activated or extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase kinase (MEK)-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway caused increased abundance of BIM, whereas antagonizing the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-AKT pathway triggered nuclear translocation of the FOXO transcription factors, which directly activated the PUMA promoter. In a mouse breast tumor model, the abundance of PUMA and BIM was increased after inactivation of HER2. Moreover, deficiency of Bim or Puma impaired caspase activation and reduced tumor regression caused by inactivation of HER2. Similarly, deficiency of Puma impeded the regression of EGFR(L858R)-driven mouse lung tumors upon inactivation of the EGFR-activating mutant. Overall, our study identified PUMA and BIM as the sentinels that interconnect kinase signaling networks and the mitochondrion-dependent apoptotic program, which offers therapeutic insights for designing novel cell death mechanism-based anticancer strategies.
Figures

References
-
- Sellers WR. A blueprint for advancing genetics-based cancer therapy. Cell. 2011;147:26–31. - PubMed
-
- Weinstein IB. Cancer. Addiction to oncogenes—The Achilles heal of cancer. Science. 2002;297:63–64. - PubMed
-
- Youle RJ, Strasser A. The BCL-2 protein family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008;9:47–59. - PubMed
-
- Wang X. The expanding role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev. 2001;15:2922–2933. - PubMed
-
- Letai A, Bassik MC, Walensky LD, Sorcinelli MD, Weiler S, Korsmeyer SJ. Distinct BH3 domains either sensitize or activate mitochondrial apoptosis, serving as prototype cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:183–192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

