Smoothened oligomerization/higher order clustering in lipid rafts is essential for high Hedgehog activity transduction
- PMID: 23532857
- PMCID: PMC3642308
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.399477
Smoothened oligomerization/higher order clustering in lipid rafts is essential for high Hedgehog activity transduction
Abstract
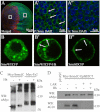
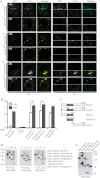
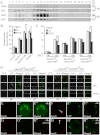
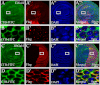
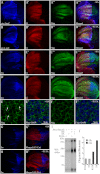
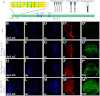
The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway plays evolutionarily conserved roles in controlling embryonic development and tissue homeostasis, and its dysregulation has been implicated in many human diseases including congenital disorder and cancer. The Hh pathway has a unique signal reception system that includes two membrane proteins, the receptor Patched (Ptc) and the transducer Smoothened (Smo). In the Hh signaling cascade, Smo plays a critical role in controlling transduction of Hh gradient signal from the outside into the inside of cells. Although the Smo downstream signal transduction has been intensively studied, the mechanism by which Smo on the plasma membrane is regulated has not been fully understood. As a specific membrane structure of metazoan cells, lipid rafts act as a platform to regulate signal transduction by forming a nanoscale cluster through protein-protein or protein-lipid interactions. However, it remains largely unknown whether lipid rafts are also involved in the regulation of Hh signal transduction. Here, we show that Smo extracellular domain (N terminus) and transmembrane domains form oligomers/higher order clusters in response to Hh signal. Furthermore, we identify that lipid rafts on the plasma membrane are essential for high level activity of Smo during the Hh signal transduction. Finally, our observation suggests that oligomerization/higher order clustering of Smo C-terminal cytoplasmic tail (C-tail) is essential for the transduction of high level Hh signal. Collectively, our data support that in response to Hh gradient signals, Smo transduces high level Hh signal by forming oligomers/higher order clusters in the lipid rafts of cell plasma membrane.
Keywords: Cancer; Drosophila; Hedgehog; Lipid Raft; Oligomer; Signal Transduction; Smo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drosophila Vps36 regulates Smo trafficking in Hedgehog signaling.J Cell Sci. 2013 Sep 15;126(Pt 18):4230-8. doi: 10.1242/jcs.128603. Epub 2013 Jul 10. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23843610
-
Transduction of the Hedgehog signal through the dimerization of Fused and the nuclear translocation of Cubitus interruptus.Cell Res. 2011 Oct;21(10):1436-51. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.136. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21844892 Free PMC article.
-
G protein Galphai functions immediately downstream of Smoothened in Hedgehog signalling.Nature. 2008 Dec 18;456(7224):967-70. doi: 10.1038/nature07459. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18987629 Free PMC article.
-
Transducing the Hedgehog signal across the plasma membrane.Fly (Austin). 2007 Nov-Dec;1(6):333-6. doi: 10.4161/fly.5570. Epub 2007 Nov 15. Fly (Austin). 2007. PMID: 18820483 Review.
-
Mechanisms of Smoothened Regulation in Hedgehog Signaling.Cells. 2021 Aug 20;10(8):2138. doi: 10.3390/cells10082138. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440907 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rafting Down the Metastatic Cascade: The Role of Lipid Rafts in Cancer Metastasis, Cell Death, and Clinical Outcomes.Cancer Res. 2021 Jan 1;81(1):5-17. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2199. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 32999001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRAF3-interacting JNK-activating modulator promotes inflammation by stimulating translocation of Toll-like receptor 4 to lipid rafts.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 22;294(8):2744-2756. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003137. Epub 2018 Dec 20. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30573680 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid raft involvement in signal transduction in cancer cell survival, cell death and metastasis.Cell Prolif. 2022 Jan;55(1):e13167. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13167. Epub 2021 Dec 22. Cell Prolif. 2022. PMID: 34939255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adaptive lipid packing and bioactivity in membrane domains.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 23;10(4):e0123930. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123930. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25905447 Free PMC article.
-
Towards Precision Oncology: The Role of Smoothened and Its Variants in Cancer.J Pers Med. 2022 Oct 5;12(10):1648. doi: 10.3390/jpm12101648. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36294790 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ingham P. W., McMahon A. P. (2001) Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev. 15, 3059–3087 - PubMed
-
- Ingham P. W., Nakano Y., Seger C. (2011) Mechanisms and functions of Hedgehog signalling across the metazoa. Nat. Rev. 12, 393–406 - PubMed
-
- Hooper J. E., Scott M. P. (1989) The Drosophila patched gene encodes a putative membrane protein required for segmental patterning. Cell 59, 751–765 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

