Brief alcohol exposure alters transcription in astrocytes via the heat shock pathway
- PMID: 23533150
- PMCID: PMC3607153
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.125
Brief alcohol exposure alters transcription in astrocytes via the heat shock pathway
Abstract
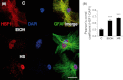
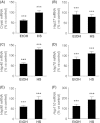
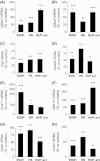
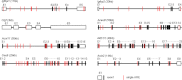
Astrocytes are critical for maintaining homeostasis in the central nervous system (CNS), and also participate in the genomic response of the brain to drugs of abuse, including alcohol. In this study, we investigated ethanol regulation of gene expression in astrocytes. A microarray screen revealed that a brief exposure of cortical astrocytes to ethanol increased the expression of a large number of genes. Among the alcohol-responsive genes (ARGs) are glial-specific immune response genes, as well as genes involved in the regulation of transcription, cell proliferation, and differentiation, and genes of the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix. Genes involved in metabolism were also upregulated by alcohol exposure, including genes associated with oxidoreductase activity, insulin-like growth factor signaling, acetyl-CoA, and lipid metabolism. Previous microarray studies performed on ethanol-treated hepatocyte cultures and mouse liver tissue revealed the induction of almost identical classes of genes to those identified in our microarray experiments, suggesting that alcohol induces similar signaling mechanisms in the brain and liver. We found that acute ethanol exposure activated heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) in astrocytes, as demonstrated by the translocation of this transcription factor to the nucleus and the induction of a family of known HSF1-dependent genes, the heat shock proteins (Hsps). Transfection of a constitutively transcriptionally active Hsf1 construct into astrocytes induced many of the ARGs identified in our microarray study supporting the hypothesis that HSF1 transcriptional activity, as part of the heat shock cascade, may mediate the ethanol induction of these genes. These data indicate that acute ethanol exposure alters gene expression in astrocytes, in part via the activation of HSF1 and the heat shock cascade.
Keywords: Alcohol; alcohol response element; astrocytes; gene expression; glia; heat shock factor 1; microarray.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Alcohol regulates gene expression in neurons via activation of heat shock factor 1.J Neurosci. 2007 Nov 21;27(47):12957-66. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4142-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 18032669 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol induces synaptotagmin 1 expression in neurons via activation of heat shock factor 1.Neuroscience. 2011 Oct 13;193:63-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.07.035. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21816209 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol protects the CNS by activating HSF1 and inducing the heat shock proteins.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Nov 20;713:134507. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134507. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 31541723 Review.
-
Cadmium-responsive element of the human heme oxygenase-1 gene mediates heat shock factor 1-dependent transcriptional activation.J Biol Chem. 2007 Mar 23;282(12):8715-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609427200. Epub 2007 Jan 23. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17244614
-
Heat shock factor 1 (HSF1)-targeted anticancer therapeutics: overview of current preclinical progress.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019 May;23(5):369-377. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2019.1602119. Epub 2019 Apr 7. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019. PMID: 30931649 Review.
Cited by
-
Perineurial Barrier Glia Physically Respond to Alcohol in an Akap200-Dependent Manner to Promote Tolerance.Cell Rep. 2018 Feb 13;22(7):1647-1656. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.01.049. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29444420 Free PMC article.
-
Blood and brain gene expression signatures of chronic intermittent ethanol consumption in mice.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Feb 17;18(2):e1009800. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009800. eCollection 2022 Feb. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 35176017 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Hippocampal Neuroimmune Response to Binge-Like Ethanol Consumption in the Drinking in the Dark Model.Neuroimmunomodulation. 2019;26(1):19-32. doi: 10.1159/000495210. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2019. PMID: 30625475 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte-specific transcriptome responses to chronic ethanol consumption.Pharmacogenomics J. 2018 Jul;18(4):578-589. doi: 10.1038/s41397-017-0012-2. Epub 2018 Jan 5. Pharmacogenomics J. 2018. PMID: 29305589 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytic transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms of drug addiction.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2024 May;131(5):409-424. doi: 10.1007/s00702-023-02716-4. Epub 2023 Nov 8. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2024. PMID: 37940687 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acquaah-Mensah GK, Leslie SW, Kehrer JP. Acute exposure of cerebellar granule neurons to ethanol suppresses stress-activated protein kinase-1 and concomitantly induces AP-1. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2001;175:10–18. - PubMed
-
- Adamo M, Roberts CT, Jr, LeRoith D. How distinct are the insulin and insulin-like growth factor I signalling systems? BioFactors. 1992;3:151–157. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed Z, Shaw G, Sharma VP, Yang C, McGowan E, Dickson DW. Actin-binding proteins coronin-1a and IBA-1 are effective microglial markers for immunohistochemistry. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2007;55:687–700. - PubMed
-
- Alciato F, Sainaghi PP, Sola D, Castello L, Avanzi GC. TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-1 expression is inhibited by GAS6 in monocytes/macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010;87:869–875. - PubMed
-
- Andres-Barquin PJ, Hernandez MC, Israel MA. Id4 expression induces apoptosis in astrocytic cultures and is down-regulated by activation of the cAMP-dependent signal transduction pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 1999;247:347–355. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

