De-repression of PDGFRβ transcription promotes acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in glioblastoma patients
- PMID: 23533263
- PMCID: PMC3651754
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0502
De-repression of PDGFRβ transcription promotes acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in glioblastoma patients
Abstract
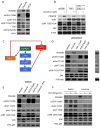
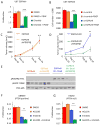
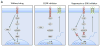
Acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) represents a major challenge for personalized cancer therapy. Multiple genetic mechanisms of acquired TKI resistance have been identified in several types of human cancer. However, the possibility that cancer cells may also evade treatment by co-opting physiologically regulated receptors has not been addressed. Here, we show the first example of this alternate mechanism in brain tumors by showing that EGF receptor (EGFR)-mutant glioblastomas (GBMs) evade EGFR TKIs by transcriptionally de-repressing platelet-derived growth factor receptor β (PDGFRβ). Mechanistic studies show that EGFRvIII signaling actively suppresses PDGFRβ transcription in an mTORC1- and extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent manner. Genetic or pharmacologic inhibition of oncogenic EGFR renders GBMs dependent on the consequently de-repressed PDGFRβ signaling for growth and survival. Importantly, combined inhibition of EGFR and PDGFRβ signaling potently suppresses tumor growth in vivo. These data identify a novel, nongenetic TKI resistance mechanism in brain tumors and provide compelling rationale for combination therapy.
Significance: These results provide the fi rst clinical and biologic evidence for receptor tyrosinekinase (RTK) "switching" as a mechanism of resistance to EGFR inhibitors in GBM and provide a molecular explanation of how tumors can become "addicted" to a non amplified, nonmutated, physiologically regulated RTK to evade targeted treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. Mischel and Cloughesy served on an advisory board for Celgene’s mTOR kinase inhibitor program. Dr. Mischel and Cloughesy also collaborated with Celgene and Sanofi through research contracts on their mTOR kinase, and PI3K/mTOR kinase inhibitor clinical trials. Dr. Kornblum collaborated with Celgene on a research contract for the mTOR kinase inhibitor program. The authors are not aware of any other potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–500. - PubMed
-
- Mellinghoff IK, Wang MY, Vivanco I, Haas-Kogan DA, Zhu S, Dia EQ, et al. Molecular determinants of the response of glioblastomas to EGFR kinase inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2012–24. - PubMed
-
- Ang KK, Berkey BA, Tu X, Zhang HZ, Katz R, Hammond EH, et al. Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor expression on survival and pattern of relapse in patients with advanced head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2002;62:7350–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS050151/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008042/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA095616/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA151819/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009120/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA119347/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NS73831/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA041996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-CA95616/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32CA009120-35/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA119347/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052563/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS073831/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- CA41996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA23100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

