Targeted inhibition of the molecular chaperone Hsp90 overcomes ALK inhibitor resistance in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 23533265
- PMCID: PMC4086149
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0440
Targeted inhibition of the molecular chaperone Hsp90 overcomes ALK inhibitor resistance in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
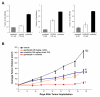
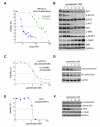
EML4-ALK gene rearrangements define a unique subset of patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC), and the clinical success of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitor crizotinib in this population has become a paradigm for molecularly targeted therapy. Here, we show that the Hsp90 inhibitor ganetespib induced loss of EML4-ALK expression and depletion of multiple oncogenic signaling proteins in ALK-driven NSCLC cells, leading to greater in vitro potency, superior antitumor efficacy, and prolonged animal survival compared with results obtained with crizotinib. In addition, combinatorial benefit was seen when ganetespib was used with other targeted ALK agents both in vitro and in vivo. Importantly, ganetespib overcame multiple forms of crizotinib resistance, including secondary ALK mutations, consistent with activity seen in a patient with crizotinib-resistant NSCLC. Cancer cells driven by ALK amplification and oncogenic rearrangements of ROS1 and RET kinase genes were also sensitive to ganetespib exposure. Taken together, these results highlight the therapeutic potential of ganetespib for ALK-driven NSCLC.
Significance: In addition to direct kinase inhibition, pharmacologic blockade of the molecular chaperone Hsp90 is emerging as a promising approach for treating tumors driven by oncogenic rearrangements of ALK. The bioactivity profi le of ganetespib presented here underscores a new therapeutic opportunity to target ALK and overcome multiple mechanisms of resistance in patients with ALK-positive NSCLC.
©2013 AACR.
Figures





References
-
- Ramalingam SS, Owonikoko TK, Khuri FR. Lung cancer: New biological insights and recent therapeutic advances. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:91–112. - PubMed
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561–6. - PubMed
-
- Choi YL, Takeuchi K, Soda M, Inamura K, Togashi Y, Hatano S, et al. Identification of novel isoforms of the EML4-ALK transforming gene in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68:4971–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

