Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Associated with FOLFOX Chemotherapy
- PMID: 23533871
- PMCID: PMC3600224
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/306983
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Associated with FOLFOX Chemotherapy
Abstract
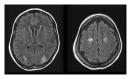
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is a clinicoradiologic entity characterized by headaches, altered mental status, seizures, visual loss, and characteristic imaging pattern in brain MRI. The cause of PRES is not yet understood. We report a case of a 27-year-old woman that developed PRES after the use of FOLFOX 5 (oxaliplatin/5-Fluoracil/Leucovorin) chemotherapy for a colorectal cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, et al. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1996;334(8):494–500. - PubMed
-
- Sheth RD, Riggs JE, Bodenstenier JB, Gutierrez AR, Ketonen LM, Ortiz OA. Parietal occipital edema in hypertensive encephalopathy: a pathogenic mechanism. European Neurology. 1996;36(1):25–28. - PubMed
-
- Hauser RA, Lacey DM, Knight MR. Hypertensive encephalopathy: magnetic resonance imaging demonstration of reversible cortical and white matter lesions. Archives of Neurology. 1988;45(10):1078–1083. - PubMed
-
- Schaefer PW, Buonanno FS, Gonzalez RG, Schwamm LH. Diffusion-weighted imaging discriminates between cytotoxic and vasogenic edema in a patient with eclampsia. Stroke. 1997;28(5):1082–1085. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources