Proteolytic elimination of N-myristoyl modifications by the Shigella virulence factor IpaJ
- PMID: 23535599
- PMCID: PMC3722872
- DOI: 10.1038/nature12004
Proteolytic elimination of N-myristoyl modifications by the Shigella virulence factor IpaJ
Abstract
Protein N-myristoylation is a 14-carbon fatty-acid modification that is conserved across eukaryotic species and occurs on nearly 1% of the cellular proteome. The ability of the myristoyl group to facilitate dynamic protein-protein and protein-membrane interactions (known as the myristoyl switch) makes it an essential feature of many signal transduction systems. Thus pathogenic strategies that facilitate protein demyristoylation would markedly alter the signalling landscape of infected host cells. Here we describe an irreversible mechanism of protein demyristoylation catalysed by invasion plasmid antigen J (IpaJ), a previously uncharacterized Shigella flexneri type III effector protein with cysteine protease activity. A yeast genetic screen for IpaJ substrates identified ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF)1p and ARF2p, small molecular mass GTPases that regulate cargo transport through the Golgi apparatus. Mass spectrometry showed that IpaJ cleaved the peptide bond between N-myristoylated glycine-2 and asparagine-3 of human ARF1, thereby providing a new mechanism for host secretory inhibition by a bacterial pathogen. We further demonstrate that IpaJ cleaves an array of N-myristoylated proteins involved in cellular growth, signal transduction, autophagasome maturation and organelle function. Taken together, these findings show a previously unrecognized pathogenic mechanism for the site-specific elimination of N-myristoyl protein modification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

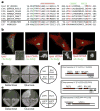

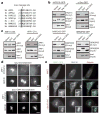
Comment in
-
Bacterial virulence: IpaJ trims the fat.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013 May;11(5):300. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3023. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23588246 No abstract available.
References
-
- Farazi TA, Waksman G, Gordon JI. The biology and enzymology of protein N-myristoylation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:39501–39504. - PubMed
-
- McLaughlin S, Aderem A. The myristoyl-electrostatic switch: a modulator of reversible protein-membrane interactions. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995;20:272–276. - PubMed
-
- Dong N, et al. Structurally distinct bacterial TBC-like GAPs link Arf GTPase to Rab1 inactivation to counteract host defenses. Cell. 2012;150:1029–1041. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

