Multiple independent variants at the TERT locus are associated with telomere length and risks of breast and ovarian cancer
- PMID: 23535731
- PMCID: PMC3670748
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2566
Multiple independent variants at the TERT locus are associated with telomere length and risks of breast and ovarian cancer
Abstract
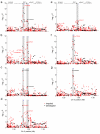
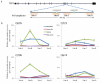
TERT-locus SNPs and leukocyte telomere measures are reportedly associated with risks of multiple cancers. Using the Illumina custom genotyping array iCOGs, we analyzed ∼480 SNPs at the TERT locus in breast (n = 103,991), ovarian (n = 39,774) and BRCA1 mutation carrier (n = 11,705) cancer cases and controls. Leukocyte telomere measurements were also available for 53,724 participants. Most associations cluster into three independent peaks. The minor allele at the peak 1 SNP rs2736108 associates with longer telomeres (P = 5.8 × 10(-7)), lower risks for estrogen receptor (ER)-negative (P = 1.0 × 10(-8)) and BRCA1 mutation carrier (P = 1.1 × 10(-5)) breast cancers and altered promoter assay signal. The minor allele at the peak 2 SNP rs7705526 associates with longer telomeres (P = 2.3 × 10(-14)), higher risk of low-malignant-potential ovarian cancer (P = 1.3 × 10(-15)) and greater promoter activity. The minor alleles at the peak 3 SNPs rs10069690 and rs2242652 increase ER-negative (P = 1.2 × 10(-12)) and BRCA1 mutation carrier (P = 1.6 × 10(-14)) breast and invasive ovarian (P = 1.3 × 10(-11)) cancer risks but not via altered telomere length. The cancer risk alleles of rs2242652 and rs10069690, respectively, increase silencing and generate a truncated TERT splice variant.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA116201/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA128978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C12292/A11174/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- BREAST CANCER NOW RESEARCH CENTRE/BBC_/Breast Cancer Now/United Kingdom
- 076113/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P30 CA076292/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA083918/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA116201/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C1287/A12014/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P30 CA016520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148112/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 15960/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- RC4 CA153828/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA087538/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C1287/A10710/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 11174/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P30 CA072720/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA070867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16565/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA092447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 11022/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA128978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 CA122443/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA149429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 13086/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C1287/A9540/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 10118/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C1287/A10118/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P30 CA071789/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA112523/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA136393/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16561/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

