An initial and rapid step of lytic granule secretion precedes microtubule organizing center polarization at the cytotoxic T lymphocyte/target cell synapse
- PMID: 23536289
- PMCID: PMC3625254
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1218640110
An initial and rapid step of lytic granule secretion precedes microtubule organizing center polarization at the cytotoxic T lymphocyte/target cell synapse
Abstract
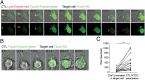
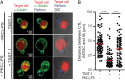
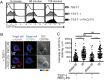
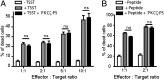
It is presently assumed that lethal hit delivery by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) is mechanistically linked to centrosome polarization toward target cells, leading to dedicated release of lytic granules within a confined secretory domain. Here we provide three lines of evidence showing that this mechanism might not apply as a general paradigm for lethal hit delivery. First, in CTLs stimulated with immobilized peptide-MHC complexes, lytic granules and microtubule organizing center localization into synaptic areas are spatio-temporally dissociated, as detected by total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy. Second, in many CTL/target cell conjugates, lytic granule secretion precedes microtubule polarization and can be detected during the first minute after cell-cell contact. Third, inhibition of microtubule organizing center and centrosome polarization impairs neither lytic granule release at the CTL synapse nor killing efficiency. Our results broaden current views of CTL biology by revealing an extremely rapid step of lytic granule secretion and by showing that microtubule organizing center polarization is dispensable for efficient lethal hit delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Law RH, et al. The structural basis for membrane binding and pore formation by lymphocyte perforin. Nature. 2010;468(7322):447–451. - PubMed
-
- de Saint Basile G, Ménasché G, Fischer A. Molecular mechanisms of biogenesis and exocytosis of cytotoxic granules. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10(8):568–579. - PubMed
-
- Purbhoo MA, Irvine DJ, Huppa JB, Davis MM. T cell killing does not require the formation of a stable mature immunological synapse. Nat Immunol. 2004;5(5):524–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

