Bazedoxifene exhibits antiestrogenic activity in animal models of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer: implications for treatment of advanced disease
- PMID: 23536434
- PMCID: PMC3643989
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3771
Bazedoxifene exhibits antiestrogenic activity in animal models of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer: implications for treatment of advanced disease
Abstract
Purpose: There is compelling evidence to suggest that drugs that function as pure estrogen receptor (ER-α) antagonists, or that downregulate the expression of ER-α, would have clinical use in the treatment of advanced tamoxifen- and aromatase-resistant breast cancer. Although such compounds are currently in development, we reasoned, based on our understanding of ER-α pharmacology, that there may already exist among the most recently developed selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERM) compounds that would have usage as breast cancer therapeutics. Thus, our objective was to identify among available SERMs those with unique pharmacologic activities and to evaluate their potential clinical use with predictive models of advanced breast cancer.
Experimental design: A validated molecular profiling technology was used to classify clinically relevant SERMs based on their impact on ER-α conformation. The functional consequences of these observed mechanistic differences on (i) gene expression, (ii) receptor stability, and (iii) activity in cellular and animal models of advanced endocrine-resistant breast cancer were assessed.
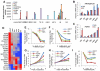
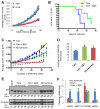
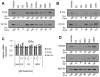
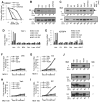
Results: The high-affinity SERM bazedoxifene was shown to function as a pure ER-α antagonist in cellular models of breast cancer and effectively inhibited the growth of both tamoxifen-sensitive and -resistant breast tumor xenografts. Interestingly, bazedoxifene induced a unique conformational change in ER-α that resulted in its proteasomal degradation, although the latter activity was dispensable for its antagonist efficacy.
Conclusion: Bazedoxifene was recently approved for use in the European Union for the treatment of osteoporosis and thus may represent a near-term therapeutic option for patients with advanced breast cancer.
©2013 AACR.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A new class of small molecule estrogen receptor-alpha antagonists that overcome anti-estrogen resistance.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 1;6(38):40388-404. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6323. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26575173 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of SERD/SERM Hybrid-CDK4/6 Inhibitor Combinations in Models of Endocrine Therapy-Resistant Breast Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 15;21(22):5121-5130. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0360. Epub 2015 May 19. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25991817 Free PMC article.
-
OCT-4: a novel estrogen receptor-α collaborator that promotes tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells.Oncogene. 2016 Nov 3;35(44):5722-5734. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.105. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 27065334
-
The use of selective estrogen receptor modulators and selective estrogen receptor down-regulators in breast cancer.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Mar;18(1):47-66. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2003.08.002. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004. PMID: 14687597 Review.
-
Selective estrogen receptor modulators and the combination therapy conjugated estrogens/bazedoxifene: A review of effects on the breast.Post Reprod Health. 2015 Sep;21(3):112-21. doi: 10.1177/2053369115599090. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Post Reprod Health. 2015. PMID: 26289836 Review.
Cited by
-
Estrogen Receptor Bio-Activities Determine Clinical Endocrine Treatment Options in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Jan-Dec;21:15330338221090351. doi: 10.1177/15330338221090351. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 35450488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Emerging Role of ESR1 Mutations in Luminal Breast Cancer as a Prognostic and Predictive Biomarker of Response to Endocrine Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 28;11(12):1894. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121894. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31795152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simulation with cells in vitro of tamoxifen treatment in premenopausal breast cancer patients with different CYP2D6 genotypes.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Dec;171(24):5624-35. doi: 10.1111/bph.12864. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25073551 Free PMC article.
-
Estradiol and Estrogen-like Alternative Therapies in Use: The Importance of the Selective and Non-Classical Actions.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 6;10(4):861. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040861. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Bazedoxifene and Conjugated Estrogen (Duavee) on Breast Cancer Risk Biomarkers in High-Risk Women: A Pilot Study.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2019 Oct;12(10):711-720. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-19-0315. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2019. PMID: 31420361 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Kvinnsland S, Anker G, Dirix LY, Bonneterre J, Prove AM, Wilking N, et al. High activity and tolerability demonstrated for exemestane in postmenopausal women with metastatic breast cancer who had previously failed on tamoxifen treatment. Eur J Cancer. 2000;36:976–82. - PubMed
-
- Dodwell D, Wardley A, Johnston S. Postmenopausal advanced breast cancer: options for therapy after tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors. Breast. 2006;15:584–94. - PubMed
-
- Goss PE, Ingle JN, Martino S, Robert NJ, Muss HB, Piccart MJ, et al. A randomized trial of letrozole in postmenopausal women after five years of tamoxifen therapy for early-stage breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1793–802. - PubMed
-
- Brodie A, Jelovac D, Sabnis G, Long B, Macedo L, Goloubeva O. Model systems: mechanisms involved in the loss of sensitivity to letrozole. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2005;95:41–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

