IL-27 receptor signaling regulates CD4+ T cell chemotactic responses during infection
- PMID: 23536628
- PMCID: PMC3886378
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202916
IL-27 receptor signaling regulates CD4+ T cell chemotactic responses during infection
Abstract
IL-27 exerts pleiotropic suppressive effects on naive and effector T cell populations during infection and inflammation. Surprisingly, however, the role of IL-27 in restricting or shaping effector CD4(+) T cell chemotactic responses, as a mechanism to reduce T cell-dependent tissue inflammation, is unknown. In this study, using Plasmodium berghei NK65 as a model of a systemic, proinflammatory infection, we demonstrate that IL-27R signaling represses chemotaxis of infection-derived splenic CD4(+) T cells in response to the CCR5 ligands, CCL4 and CCL5. Consistent with these observations, CCR5 was expressed on significantly higher frequencies of splenic CD4(+) T cells from malaria-infected, IL-27R-deficient (WSX-1(-/-)) mice than from infected wild-type mice. We find that IL-27 signaling suppresses splenic CD4(+) T cell CCR5-dependent chemotactic responses during infection by restricting CCR5 expression on CD4(+) T cell subtypes, including Th1 cells, and also by controlling the overall composition of the CD4(+) T cell compartment. Diminution of the Th1 response in infected WSX-1(-/-) mice in vivo by neutralization of IL-12p40 attenuated CCR5 expression by infection-derived CD4(+) T cells and also reduced splenic CD4(+) T cell chemotaxis toward CCL4 and CCL5. These data reveal a previously unappreciated role for IL-27 in modulating CD4(+) T cell chemotactic pathways during infection, which is related to its capacity to repress Th1 effector cell development. Thus, IL-27 appears to be a key cytokine that limits the CCR5-CCL4/CCL5 axis during inflammatory settings.
Figures




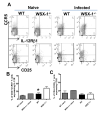
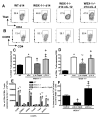
References
-
- Yoshida H, Nakaya M, Miyazaki Y. Interleukin 27: a double-edged sword for offense and defense. J Leukoc Biol. 2009;86:1295–303. - PubMed
-
- Hall AO, Silver JS, Hunter CA. The immunobiology of IL-27. Adv Immunol. 2012;115:1–44. - PubMed
-
- Findlay EG, Greig R, Stumhofer JS, Hafalla JC, de Souza JB, Saris CJ, Hunter CA, Riley EM, Couper KN. Essential role for IL-27 receptor signaling in prevention of Th1-mediated immunopathology during malaria infection. J Immunol. 2010;185:2482–92. - PubMed
-
- Villarino A, Hibbert L, Lieberman L, Wilson E, Mak T, Yoshida H, Kastelein RA, Saris C, Hunter CA. The IL-27R (WSX-1) is required to suppress T cell hyperactivity during infection. Immunity. 2003;19:645–55. - PubMed
-
- Hamano S, Himeno K, Miyazaki Y, Ishii K, Yamanaka A, Takeda A, Zhang M, Hisaeda H, Mak TW, Yoshimura A, Yoshida H. WSX-1 is required for resistance to Trypanosoma cruzi infection by regulation of proinflammatory cytokine production. Immunity. 2003;19:657–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G0900487/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 004161/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/I020950/2/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 020950/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/G004161/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

