Identification and Characterisation CRN Effectors in Phytophthora capsici Shows Modularity and Functional Diversity
- PMID: 23536880
- PMCID: PMC3607596
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059517
Identification and Characterisation CRN Effectors in Phytophthora capsici Shows Modularity and Functional Diversity
Abstract
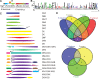
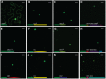
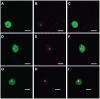
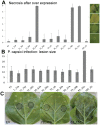
Phytophthora species secrete a large array of effectors during infection of their host plants. The Crinkler (CRN) gene family encodes a ubiquitous but understudied class of effectors with possible but as of yet unknown roles in infection. To appreciate CRN effector function in Phytophthora, we devised a simple Crn gene identification and annotation pipeline to improve effector prediction rates. We predicted 84 full-length CRN coding genes and assessed CRN effector domain diversity in sequenced Oomycete genomes. These analyses revealed evidence of CRN domain innovation in Phytophthora and expansion in the Peronosporales. We performed gene expression analyses to validate and define two classes of CRN effectors, each possibly contributing to infection at different stages. CRN localisation studies revealed that P. capsici CRN effector domains target the nucleus and accumulate in specific sub-nuclear compartments. Phenotypic analyses showed that few CRN domains induce necrosis when expressed in planta and that one cell death inducing effector, enhances P. capsici virulence on Nicotiana benthamiana. These results suggest that the CRN protein family form an important class of intracellular effectors that target the host nucleus during infection. These results combined with domain expansion in hemi-biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens, suggests specific contributions to pathogen lifestyles. This work will bolster CRN identification efforts in other sequenced oomycete species and set the stage for future functional studies towards understanding CRN effector functions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Bozkurt TO, Schornack S, Banfield MJ, Kamoun S (2012) Oomycetes, effectors, and all that jazz. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 15: 9. - PubMed
-
- Birch PR, Rehmany AP, Pritchard L, Kamoun S, Beynon JL (2006) Trafficking arms: oomycete effectors enter host plant cells. Trends Microbiol 14: 8–11. - PubMed
-
- Kamoun S (2007) Groovy times: filamentous pathogen effectors revealed. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10: 358–365. - PubMed
-
- Stassen JHM, Van den Ackerveken G (2011) How do oomycete effectors interfere with plant life? Current Opinion in Plant Biology 14: 407–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

