Assessment by meta-analysis of interferon-gamma for the diagnosis of tuberculous peritonitis
- PMID: 23539367
- PMCID: PMC3602483
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i10.1645
Assessment by meta-analysis of interferon-gamma for the diagnosis of tuberculous peritonitis
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the performance and diagnostic accuracy of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) for tuberculous peritonitis (TBP) by meta-analysis.
Methods: A systematic search of English language studies was performed. We searched the following electronic databases: MEDLINE, EMBASE, Web of Science, BIOSIS, LILACS and the Cochrane Library. The Standards for Reporting Diagnostic Accuracy initiative and Quality Assessment for Studies of Diagnostic Accuracy tool were used to assess the methodological quality of the studies. Sensitivity, specificity, and other measures of the accuracy of IFN-γ concentration in the diagnosis of peritoneal effusion were pooled using random-effects models. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were applied to summarize overall test performance. Two reviewers independently judged study eligibility while screening the citations.
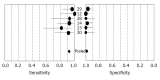
Results: Six studies met the inclusion criteria. The average inter-rater agreement between the two reviewers for items in the quality checklist was 0.92. Analysis of IFN-γ level for TBP diagnosis yielded a summary estimate: sensitivity, 0.93 (95%CI, 0.87-0.97); specificity, 0.99 (95%CI, 0.97-1.00); positive likelihood ratio (PLR), 41.49 (95%CI, 18.80-91.55); negative likelihood ratio (NLR), 0.11 (95%CI, 0.06-0.19); and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), 678.02 (95%CI, 209.91-2190.09). χ(2) values of the sensitivity, specificity, PLR, NLR and DOR were 5.66 (P = 0.3407), 6.37 (P = 0.2715), 1.38 (P = 0.9265), 5.46 (P = 0.3621) and 1.42 (P = 0.9220), respectively. The summary receiver ROC curve was positioned near the desirable upper left corner and the maximum joint sensitivity and specificity was 0.97. The area under the curve was 0.99. The evaluation of publication bias was not significant (P = 0.922).
Conclusion: IFN-γ may be a sensitive and specific marker for the accurate diagnosis of TBP. The level of IFN-γ may contribute to the accurate differentiation of tuberculosis (TB) ascites from non-TB ascites.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Interferon-gamma; Meta-analysis; Tuberculosis; Tuberculous peritonitis.
Figures

References
-
- Sharma SK, Mohan A. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Indian J Med Res. 2004;120:316–353. - PubMed
-
- Sharma MP, Bhatia V. Abdominal tuberculosis. Indian J Med Res. 2004;120:305–315. - PubMed
-
- Riquelme A, Calvo M, Salech F, Valderrama S, Pattillo A, Arellano M, Arrese M, Soza A, Viviani P, Letelier LM. Value of adenosine deaminase (ADA) in ascitic fluid for the diagnosis of tuberculous peritonitis: a meta-analysis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;40:705–710. - PubMed
-
- Lingenfelser T, Zak J, Marks IN, Steyn E, Halkett J, Price SK. Abdominal tuberculosis: still a potentially lethal disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993;88:744–750. - PubMed
-
- Inadomi JM, Kapur S, Kinkhabwala M, Cello JP. The laparoscopic evaluation of ascites. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2001;11:79–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

