RETRACTED: Collagen prolyl hydroxylases are essential for breast cancer metastasis
- PMID: 23539444
- PMCID: PMC3674184
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3963
RETRACTED: Collagen prolyl hydroxylases are essential for breast cancer metastasis
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Collagen Prolyl Hydroxylases Are Essential for Breast Cancer Metastasis.Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 4;84(17):2927. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-24-2214. Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39228257 No abstract available.
Expression of concern in
-
Editor's Note: Collagen Prolyl Hydroxylases Are Essential for Breast Cancer Metastasis.Cancer Res. 2022 Mar 1;82(5):943. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-4312. Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35247897 No abstract available.
Abstract
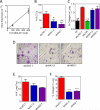
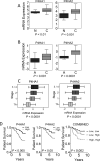
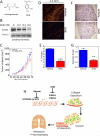
The presence of hypoxia and fibrosis within the primary tumor are two major risk factors for metastasis of human breast cancer. In this study, we demonstrate that hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activates the transcription of genes encoding collagen prolyl hydroxylases that are critical for collagen deposition by breast cancer cells. We show that expression of collagen prolyl hydroxylases promotes cancer cell alignment along collagen fibers, resulting in enhanced invasion and metastasis to lymph nodes and lungs. Finally, we establish the prognostic significance of collagen prolyl hydroxylase mRNA expression in human breast cancer biopsies and show that ethyl 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate, a prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor, decreases tumor fibrosis and metastasis in a mouse model of breast cancer.
©2013 AACR.
Figures
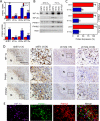
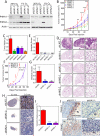
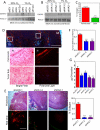
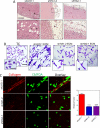
References
-
- Brahimi-Horn MC, Chiche J, Pouyssegur J. Hypoxia and cancer. J Mol Med. 2007;85:1301–7. - PubMed
-
- Dewhirst MW. Intermittent hypoxia furthers the rationale for hypoxia-inducible factor-1 targeting. Cancer Res. 2007;67:854–5. - PubMed
-
- Hiraga T, Kizaka-Kondoh S, Hirota K, Hiraoka M, Yoneda T. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 expression enhance osteolytic bone metastases of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:4157–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

