Decision making for pancreatic resection in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms
- PMID: 23539521
- PMCID: PMC3602505
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i9.1451
Decision making for pancreatic resection in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms
Abstract
Aim: To identify a practical approach for preoperative decision-making in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) of the pancreas.
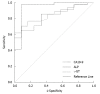
Methods: Between March 1999 and November 2006, the clinical characteristics, pathological data and computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging (CT/MRI) of 54 IPMNs cases were retrieved and analyzed. The relationships between the above data and decision-making for pancreatic resection were analyzed using SPSS 13.0 software. Univariate analysis of risk factors for malignant or invasive IPMNs was performed with regard to the following variables: carcinoembryonic antigen, carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) and the characteristics from CT/MRI images. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis for pancreatic resection was performed using significant factors from the univariate analysis.
Results: CT/MRI images, including main and mixed duct IPMNs, tumor size > 30 mm or a solid component appearance in the lesion, and preoperative serum CA19-9 > 37 U/mL had good predictive value for determining pancreatic resection (P < 0.05), but with limitations. Combining the above factors (CT/MRI images and CA19-9) improved the accuracy and sensitivity for determining pancreatic resection in IPMNs. Using ROC analysis, the area under the curve reached 0.893 (P < 0.01, 95%CI: 0.763-1.023), with a sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of 95.2%, 83.3%, 95.2% and 83.3%, respectively.
Conclusion: Combining preoperative CT/MRI images and CA19-9 level may provide useful information for surgical decision-making in IPMNs.
Keywords: Carbohydrate antigen 19-9; Computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging; Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms; Predictor; Surgical decision-making.
Figures


References
-
- Sadakari Y, Ohuchida K, Nakata K, Ohtsuka T, Aishima S, Takahata S, Nakamura M, Mizumoto K, Tanaka M. Invasive carcinoma derived from the nonintestinal type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas has a poorer prognosis than that derived from the intestinal type. Surgery. 2010;147:812–817. - PubMed
-
- Wente MN, Schmied BM, Schmidt J, Büchler MW. [Differentiated therapy for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms] Chirurg. 2009;80:7–13. - PubMed
-
- Poultsides GA, Reddy S, Cameron JL, Hruban RH, Pawlik TM, Ahuja N, Jain A, Edil BH, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Schulick RD, et al. Histopathologic basis for the favorable survival after resection of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm-associated invasive adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Ann Surg. 2010;251:470–476. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lin SC, Shan YS, Lin PW. Adequate preoperative biliary drainage is determinative to decrease postoperative infectious complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Hepatogastroenterology. 2010;57:698–705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

