Influence of metabolism on epigenetics and disease
- PMID: 23540690
- PMCID: PMC3775362
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.004
Influence of metabolism on epigenetics and disease
Abstract
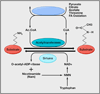
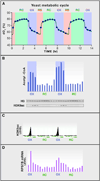
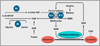
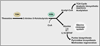
Chemical modifications of histones and DNA, such as histone methylation, histone acetylation, and DNA methylation, play critical roles in epigenetic gene regulation. Many of the enzymes that add or remove such chemical modifications are known, or might be suspected, to be sensitive to changes in intracellular metabolism. This knowledge provides a conceptual foundation for understanding how mutations in the metabolic enzymes SDH, FH, and IDH can result in cancer and, more broadly, for how alterations in metabolism and nutrition might contribute to disease. Here, we review literature pertinent to hypothetical connections between metabolic and epigenetic states in eukaryotic cells.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Adam J, Hatipoglu E, O’Flaherty L, Ternette N, Sahgal N, Lockstone H, Baban D, Nye E, Stamp GW, Wolhuter K, et al. Renal cyst formation in Fh1-deficient mice is independent of the Hif/Phd pathway: roles for fumarate in KEAP1 succination and Nrf2 signaling. Cancer Cell. 2011;20:524–537. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amary MF, Damato S, Halai D, Eskandarpour M, Berisha F, Bonar F, McCarthy S, Fantin VR, Straley KS, Lobo S, et al. Ollier disease and Maffucci syndrome are caused by somatic mosaic mutations of IDH1 and IDH2. Nat. Genet. 2011;43:1262–1265. - PubMed
-
- Andreeva VA, Touvier M, Kesse-Guyot E, Julia C, Galan P, Hercberg S. B vitamin and/or u-3 fatty acid supplementation and cancer: ancillary findings from the supplementation with folate, vitamins B6 and B12, and/or omega-3 fatty acids (SU.FOL.OM3) randomized trial. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012;172:540–547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

