Somatic mutations of the immunoglobulin framework are generally required for broad and potent HIV-1 neutralization
- PMID: 23540694
- PMCID: PMC3792590
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.018
Somatic mutations of the immunoglobulin framework are generally required for broad and potent HIV-1 neutralization
Abstract
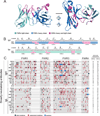
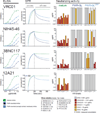
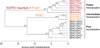
Broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) to HIV-1 can prevent infection and are therefore of great importance for HIV-1 vaccine design. Notably, bNAbs are highly somatically mutated and generated by a fraction of HIV-1-infected individuals several years after infection. Antibodies typically accumulate mutations in the complementarity determining region (CDR) loops, which usually contact the antigen. The CDR loops are scaffolded by canonical framework regions (FWRs) that are both resistant to and less tolerant of mutations. Here, we report that in contrast to most antibodies, including those with limited HIV-1 neutralizing activity, most bNAbs require somatic mutations in their FWRs. Structural and functional analyses reveal that somatic mutations in FWR residues enhance breadth and potency by providing increased flexibility and/or direct antigen contact. Thus, in bNAbs, FWRs play an essential role beyond scaffolding the CDR loops and their unusual contribution to potency and breadth should be considered in HIV-1 vaccine design.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Amit AG, Mariuzza RA, Phillips SE, Poljak RJ. Three-dimensional structure of an antigen-antibody complex at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1986;233:747–753. - PubMed
-
- Amzel LM, Poljak RJ. Three-dimensional structure of immunoglobulins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:961–997. - PubMed
-
- Batista FD, Neuberger MS. Affinity dependence of the B cell response to antigen: a threshold, a ceiling, and the importance of off-rate. Immunity. 1998;8:751–759. - PubMed
-
- Buchacher A, Predl R, Strutzenberger K, Steinfellner W, Trkola A, Purtscher M, Gruber G, Tauer C, Steindl F, Jungbauer A, et al. Generation of human monoclonal antibodies against HIV-1 proteins; electrofusion and Epstein-Barr virus transformation for peripheral blood lymphocyte immortalization. AIDS research and human retroviruses. 1994;10:359–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

