Neural correlates of rapid antidepressant response to ketamine in treatment-resistant unipolar depression: a preliminary positron emission tomography study
- PMID: 23540908
- PMCID: PMC3672258
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.02.008
Neural correlates of rapid antidepressant response to ketamine in treatment-resistant unipolar depression: a preliminary positron emission tomography study
Abstract
Background: Multiple lines of evidence support a role for the glutamatergic system in the pathophysiology of major depressive disorder (MDD). Ketamine, an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist, rapidly improves depressive symptoms in individuals with treatment-resistant depression. The neural mechanisms underlying this effect remain unknown.
Methods: In this preliminary study, 20 unmedicated participants with treatment-resistant MDD underwent positron emission tomography to measure regional cerebral glucose metabolism at baseline and following ketamine infusion (single dose of .5mg/kg intravenous over 40minutes). Metabolic data were compared between conditions using a combination of region-of-interest and voxelwise analyses, and differences were correlated with the associated antidepressant response.
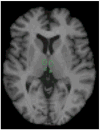
Results: Whole-brain metabolism did not change significantly following ketamine. Regional metabolism decreased significantly under ketamine in the habenula, insula, and ventrolateral and dorsolateral prefrontal cortices of the right hemisphere. Metabolism increased postketamine in bilateral occipital, right sensorimotor, left parahippocampal, and left inferior parietal cortices. Improvement in depression ratings correlated directly with change in metabolism in right superior and middle temporal gyri. Conversely, clinical improvement correlated inversely with metabolic changes in right parahippocampal gyrus and temporoparietal cortex.
Conclusions: Although preliminary, these results indicate that treatment-resistant MDD subjects showed decreased metabolism in the right habenula and the extended medial and orbital prefrontal networks in association with rapid antidepressant response to ketamine. Conversely, metabolism increased in sensory association cortices, conceivably related to the illusory phenomena sometimes experienced with ketamine. Further studies are needed to elucidate how these functional anatomical changes relate to the molecular mechanisms underlying ketamine's rapid antidepressant effects.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Berman RM, Cappiello A, Anand A, Oren DA, Heninger GR, Charney DS, et al. Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry. 2000;47:351–354. - PubMed
-
- Zarate CA, Jr, Singh JB, Carlson PJ, Brutsche NE, Ameli R, Luckenbaugh DA, et al. A randomized trial of an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63:856–864. - PubMed
-
- Trullas R, Skolnick P. Functional antagonists at the NMDA receptor complex exhibit antidepressant actions. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990;185:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Meloni D, Gambarana C, De Montis MG, Dal Pra P, Taddei I, Tagliamonte A. Dizocilpine antagonizes the effect of chronic imipramine on learned helplessness in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1993;46:423–426. - PubMed
-
- Moryl E, Danysz W, Quack G. Potential antidepressive properties of amantadine, memantine and bifemelane. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;72:394–397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

