Incidence and associated premorbid diagnoses of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis
- PMID: 23541327
- PMCID: PMC3788631
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.02.002
Incidence and associated premorbid diagnoses of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis
Abstract
Background: Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a prevalent condition with underexplored risk factors.
Objectives: We sought to determine CRS incidence and evaluate associations with a range of premorbid medical conditions for chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps (CRSsNP) and chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) using real-world clinical practice data.
Methods: Electronic health records data from 446,480 Geisinger Clinic primary care patients were used for a retrospective longitudinal cohort study for data from 2001-2010. By using logistic regression, newly diagnosed CRS cases between 2007 and 2009 were compared with frequency-matched control subjects on premorbid factors in the immediate (0-6 months), intermediate (7-24 months), and entire observed timeframes before diagnosis.
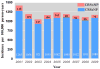
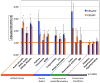
Results: The average incidence of CRS was 83 ± 13 CRSwNP cases per 100,000 person-years and 1048 ± 78 CRSsNP cases per 100,000 person-years. Between 2007 and 2009, 595 patients with incident CRSwNP and 7523 patients with incident CRSsNP were identified and compared with 8118 control subjects. Compared with control subjects and patients with CRSsNP, patients with CRSwNP were older and more likely to be male. Before diagnosis, patients with CRS had a higher prevalence of acute rhinosinusitis, allergic rhinitis, chronic rhinitis, asthma, gastroesophageal reflux disease, adenotonsillitis, sleep apnea, anxiety, and headaches (all P < .001). Patients with CRSsNP had a higher premorbid prevalence of infections of the upper and lower airway, skin/soft tissue, and urinary tract (all P < .001). In the immediate and intermediate timeframes analyzed, patients with CRS had more outpatient encounters and antibiotic prescriptions (P < .001), but guideline-recommended diagnostic testing was performed in a minority of cases.
Conclusions: Patients who are given a diagnosis of CRS have a higher premorbid prevalence of anxiety, headaches, gastroesophageal reflux disease, sleep apnea, and infections of the respiratory system and some nonrespiratory sites, which results in higher antibiotic, corticosteroid, and health care use. The use of guideline-recommended diagnostic testing for confirmation of CRS remains poor.
Copyright © 2013 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C, Alobid I, Baroody F, et al. EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology. 2012;50(1):1–12. Epub 2012/04/04. - PubMed
-
- Pleis JR, Lucas JW, Ward BW. Summary health statistics for U.S. adults: National Health Interview Survey, 2008. Vital Health Stat. 2009;10(242):1–157. Epub 2010/09/09. - PubMed
-
- Rosenfeld RM, Andes D, Bhattacharyya N, Cheung D, Eisenberg S, Ganiats TG, et al. Clinical practice guideline: adult sinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;137(3 Suppl):S1–31. Epub 2007/09/28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

