D316 is critical for the enzymatic activity and HIV-1 restriction potential of human and rhesus APOBEC3B
- PMID: 23542011
- PMCID: PMC3752335
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.03.003
D316 is critical for the enzymatic activity and HIV-1 restriction potential of human and rhesus APOBEC3B
Abstract
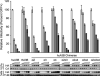
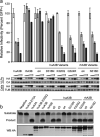
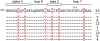
APOBEC3B is one of seven human APOBEC3 DNA cytosine deaminases that function to inhibit the replication and persistence of retroelements and retroviruses. Human APOBEC3B restricts the replication of HIV-1 in HEK293 cells, while our laboratory clone of rhesus macaque APOBEC3B did not. We mapped the restriction determinant to a single amino acid difference that alters enzymatic activity. Human APOBEC3B D316 is catalytically active and capable of restricting HIV-1 while rhesus APOBEC3B N316 is not; swapping these residues alters the activity and restriction phenotypes respectively. Genotyping of primate center rhesus macaques revealed uniform homozygosity for aspartate at position 316. Considering the C-to-T nature of the underlying mutation, we suspect that our rhesus APOBEC3B cDNA was inactivated by its own gene product during subcloning in Escherichia coli. This region has been previously characterized for its role in substrate specificity, but these data indicate it also has a fundamental role in deaminase activity.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

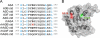
Similar articles
-
Ancestral APOBEC3B Nuclear Localization Is Maintained in Humans and Apes and Altered in Most Other Old World Primate Species.mSphere. 2022 Dec 21;7(6):e0045122. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00451-22. Epub 2022 Nov 14. mSphere. 2022. PMID: 36374108 Free PMC article.
-
Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Vif and Human APOBEC3B Interactions Resemble Those between HIV-1 Vif and Human APOBEC3G.J Virol. 2018 May 29;92(12):e00447-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00447-18. Print 2018 Jun 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29618650 Free PMC article.
-
APOBEC3B lysine residues are dispensable for DNA cytosine deamination, HIV-1 restriction, and nuclear localization.Virology. 2017 Nov;511:74-81. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2017.08.025. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Virology. 2017. PMID: 28841445 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B: modern concepts in pathogenesis--APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases as effectors in innate immunity against the hepatitis B virus.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2008 Jun;21(3):298-303. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e3282fe1bb2. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18448976 Review.
-
APOBEC3B: pathological consequences of an innate immune DNA mutator.Biomed J. 2015 Mar-Apr;38(2):102-10. doi: 10.4103/2319-4170.148904. Biomed J. 2015. PMID: 25566802 Review.
Cited by
-
Enzyme cycling contributes to efficient induction of genome mutagenesis by the cytidine deaminase APOBEC3B.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 16;45(20):11925-11940. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx832. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28981865 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the N-terminal positively charged residues of the simian immunodeficiency virus Vif reveals a critical amino acid required for the antagonism of rhesus APOBEC3D, G, and H.Virology. 2014 Jan 20;449:140-9. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.10.037. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Virology. 2014. PMID: 24418547 Free PMC article.
-
Ancestral APOBEC3B Nuclear Localization Is Maintained in Humans and Apes and Altered in Most Other Old World Primate Species.mSphere. 2022 Dec 21;7(6):e0045122. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00451-22. Epub 2022 Nov 14. mSphere. 2022. PMID: 36374108 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation of the cancer genomic DNA deaminase APOBEC3B by SIV Vif.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 24;6(37):39969-79. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5483. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26544511 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of Oligonucleotide Selectivity of APOBEC3B.J Chem Inf Model. 2019 May 28;59(5):2264-2273. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00427. Epub 2018 Sep 10. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 30130104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bishop KN, Holmes RK, Sheehy AM, Davidson NO, Cho SJ, Malim MH. Cytidine deamination of retroviral DNA by diverse APOBEC proteins. Curr. Biol. 2004;14(15):1392–1396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

