Adipose-specific lipoprotein lipase deficiency more profoundly affects brown than white fat biology
- PMID: 23542081
- PMCID: PMC3656262
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.469270
Adipose-specific lipoprotein lipase deficiency more profoundly affects brown than white fat biology
Abstract
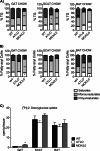
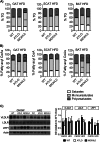
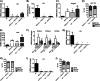
Adipose fat storage is thought to require uptake of circulating triglyceride (TG)-derived fatty acids via lipoprotein lipase (LpL). To determine how LpL affects the biology of adipose tissue, we created adipose-specific LpL knock-out (ATLO) mice, and we compared them with whole body LpL knock-out mice rescued with muscle LpL expression (MCK/L0) and wild type (WT) mice. ATLO LpL mRNA and activity were reduced, respectively, 75 and 70% in gonadal adipose tissue (GAT), 90 and 80% in subcutaneous tissue, and 84 and 85% in brown adipose tissue (BAT). ATLO mice had increased plasma TG levels associated with reduced chylomicron TG uptake into BAT and lung. ATLO BAT, but not GAT, had altered TG composition. GAT from MCK/L0 was smaller and contained less polyunsaturated fatty acids in TG, although GAT from ATLO was normal unless LpL was overexpressed in muscle. High fat diet feeding led to less adipose in MCK/L0 mice but TG acyl composition in subcutaneous tissue and BAT reverted to that of WT. Therefore, adipocyte LpL in BAT modulates plasma lipoprotein clearance, and the greater metabolic activity of this depot makes its lipid composition more dependent on LpL-mediated uptake. Loss of adipose LpL reduces fat accumulation only if accompanied by greater LpL activity in muscle. These data support the role of LpL as the "gatekeeper" for tissue lipid distribution.
Keywords: Adipocyte; Fatty Acid; Hypertriglyceridemia; Lipids; Macrophages; Obesity.
Figures



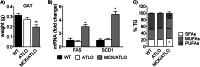
References
-
- Jacobsen B. K., Trygg K., Hjermann I., Thomassen M. S., Real C., Norum K. R. (1983) Acyl pattern of adipose tissue triglycerides, plasma free fatty acids, and diet of a group of men participating in a primary coronary prevention program (the Oslo Study). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 38, 906–913 - PubMed
-
- van Staveren W. A., Deurenberg P., Katan M. B., Burema J., de Groot L. C., Hoffmans M. D. (1986) Validity of the fatty acid composition of subcutaneous fat tissue microbiopsies as an estimate of the long-term average fatty acid composition of the diet of separate individuals. Am. J. Epidemiol. 123, 455–463 - PubMed
-
- Strawford A., Antelo F., Christiansen M., Hellerstein M. K. (2004) Adipose tissue triglyceride turnover, de novo lipogenesis, and cell proliferation in humans measured with 2H2O. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 286, E577–E588 - PubMed
-
- Goldberg I. J. (1996) Lipoprotein lipase and lipolysis: central roles in lipoprotein metabolism and atherogenesis. J. Lipid Res. 37, 693–707 - PubMed
-
- Berger G. M. (1986) Clearance defects in primary chylomicronemia: a study of tissue lipoprotein lipase activities. Metabolism 35, 1054–1061 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

