Calpains mediate axonal cytoskeleton disintegration during Wallerian degeneration
- PMID: 23542511
- PMCID: PMC3721029
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.03.009
Calpains mediate axonal cytoskeleton disintegration during Wallerian degeneration
Abstract
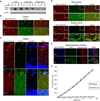
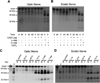
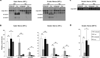
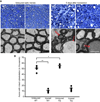
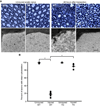
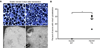
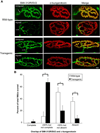
In both the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS), transected axons undergo Wallerian degeneration. Even though Augustus Waller first described this process after transection of axons in 1850, the molecular mechanisms may be shared, at least in part, by many human diseases. Early pathology includes failure of synaptic transmission, target denervation, and granular disintegration of the axonal cytoskeleton (GDC). The Ca(2+)-dependent protease calpains have been implicated in GDC but causality has not been established. To test the hypothesis that calpains play a causal role in axonal and synaptic degeneration in vivo, we studied transgenic mice that express human calpastatin (hCAST), the endogenous calpain inhibitor, in optic and sciatic nerve axons. Five days after optic nerve transection and 48 h after sciatic nerve transection, robust neurofilament proteolysis observed in wild-type controls was reduced in hCAST transgenic mice. Protection of the axonal cytoskeleton in sciatic nerves of hCAST mice was nearly complete 48 h post-transection. In addition, hCAST expression preserved the morphological integrity of neuromuscular junctions. However, compound muscle action potential amplitudes after nerve transection were similar in wild-type and hCAST mice. These results, in total, provide direct evidence that calpains are responsible for the morphological degeneration of the axon and synapse during Wallerian degeneration.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
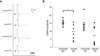
References
-
- Ai J, Liu E, Wang J, Chen Y, Yu J, Baker AJ. Calpain inhibitor MDL-28170 reduces the functional and structural deterioration of corpus callosum following fluid percussion injury. J. Neurotrauma. 2007;24:960–978. - PubMed
-
- Beirowski B, Nógrádi A, Babetto E, Garcia-Alias G, Coleman MP. Mechanisms of axonal spheroid formation in central nervous system Wallerian degeneration. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2010;69:455–472. - PubMed
-
- Bignami A, Dahl D, Nguyen BT, Crosby CJ. The fate of axonal debris in Wallerian degeneration of rat optic and sciatic nerves. Electron microscopy and immunofluorescence studies with neurofilament antisera. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1981;40:537–550. - PubMed
-
- Blumbergs PC, Scott G, Manavis J, Wainwright H, Simpson DA, McLean AJ. Topography of axonal injury as defined by amyloid precursor protein and the sector scoring method in mild and severe closed head injury. J. Neurotrauma. 1995;12:565–572. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

