Sensing and alarm function of resident memory CD8⁺ T cells
- PMID: 23542740
- PMCID: PMC3631432
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2568
Sensing and alarm function of resident memory CD8⁺ T cells
Erratum in
- Nat Immunol. 2013 Aug;14(8):876
Abstract
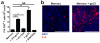
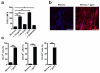
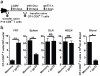
CD8(+) T cells eliminate intracellular infections through two contact-dependent effector functions: cytolysis and secretion of antiviral cytokines. Here we identify the following additional function for memory CD8(+) T cells that persist at front-line sites of microbial exposure: to serve as local sensors of previously encountered antigens that precipitate innate-like alarm signals and draw circulating memory CD8(+) T cells into the tissue. When memory CD8(+) T cells residing in the female mouse reproductive tract encountered cognate antigen, they expressed interferon-γ (IFN-γ), potentiated robust local expression of inflammatory chemokines and induced rapid recruitment of circulating memory CD8(+) T cells. Anamnestic responses in front-line tissues are thus an integrated collaboration between front-line and circulating populations of memory CD8(+) T cells, and vaccines should establish both populations to maximize rapid responses.
Figures
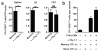
References
-
- Sallusto F, Geginat J, Lanzavecchia A. Central memory and effector memory T cell subsets: function, generation, and maintenance. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004;22:745–763. - PubMed
-
- Andrian, von UH, Mackay CR. T-cell function and migration. Two sides of the same coin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000;343:1020–1034. - PubMed
-
- Seder RA, Ahmed R. Similarities and differences in CD4+ and CD8+ effector and memory T cell generation. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:835–842. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;240:783–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

