The Role of GABAB Receptors in Morphine Self-Administration
- PMID: 23542877
- PMCID: PMC3604847
The Role of GABAB Receptors in Morphine Self-Administration
Abstract
Background: There is only little information about the effects of GABA receptors agonist and antagonist on morphine self-administration. Present study was designed to assess role of GABAB receptors in the regulation of morphine-reinforced self-administration.
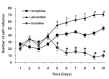
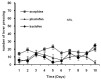
Methods: THIS STUDY WAS PERFORMED IN FOUR GROUPS OF RATS: (1) Saline group, which received saline in the self-administration session. (2) Morphine group, which received morphine in saline solution in the self-administration session. (3) Baclofen + Morphine group, which received both baclofen 20 min before self- administration test and morphine in the self-administration session. (4) Phaclofen + Morphine group, which received both phaclofen 20 min before self- administration test and morphine in the self-administration session. The number of lever pressing and self-infusion were recorded.
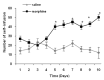
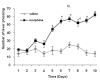
Results: Morphine significantly increased the number of active lever pressing dose dependently in self-administration session in comparative with saline group. Administration of baclofen, 20 min before morphine self-administration produced significant decrease in the initiation of morphine self-administration during all session. Conversely, pre-treatment of phaclofen increased the number of active lever pressing and self-infusion in this test.
Conclusion: Our results indicated a short-term treatment by baclofen, reduced morphine-maintenance response in a dose-dependent manner, suggesting that GABAB receptor agonists could be useful for reversing the neuroadaptations related to opiates.
Keywords: Baclofen; morphine addiction; phaclofen; self-administration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Yoon SS, Lee BH, Kim HS, Choi KH, Yun J, Jang EY, et al. Potential roles of GABA receptors in morphine self-administration in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2007;428:33–7. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki T, Nurrochmad A, Qzaki M, Khotib J, Nakamura A, Imai S, et al. Effect of the GABAB receptor agonist baclophen on the μ-opiod receptor agonist-induced antinociceptive, emetic and rewarding effects. Neuropharmacology. 2005;49:1121–31. - PubMed
-
- Dunbar SA, Karamian I, Yeatman A, Zhang J. Effect of reccurent withdrawal on spinal GABA release during chronic morphine infusion in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006;535:152–6. - PubMed
-
- Apergis-Schoute J, Pinto A, Pare D. Ulterastructural organization of medial prefronta inputs to the rhinal cortices. Eur J Neurosci. 2006;24:135–44. - PubMed
-
- Rae C, Nasrallah FA, Griffin JL, Balcar VJ. Now I know my ABC. A systems neurochemistry and functional metabolomic approach to understanding the GABAergic system. J Neurochem. 2009;109:109–16. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
