Prefrontal cortical kappa-opioid receptor modulation of local neurotransmission and conditioned place aversion
- PMID: 23542927
- PMCID: PMC3717537
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2013.76
Prefrontal cortical kappa-opioid receptor modulation of local neurotransmission and conditioned place aversion
Abstract
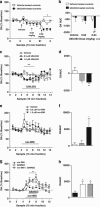
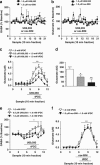
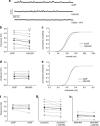
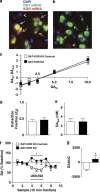
Kappa-opioid receptors (KORs) are important for motivation and other medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC)-dependent behaviors. Although KORs are present in the mPFC, their role in regulating transmission in this brain region and their contribution to KOR-mediated aversion are not known. Using in vivo microdialysis in rats and mice, we demonstrate that intra-mPFC administration of the selective KOR agonist U69,593 decreased local dopamine (DA) overflow, while reverse dialysis of the KOR antagonist nor-Binaltorphimine (nor-BNI) enhanced mPFC DA overflow. Extracellular amino-acid levels were also affected by KORs, as U69,593 reduced glutamate and GABA levels driven by the glutamate reuptake blocker, l-trans-pyrrolidine-2,4-dicarboxylate. Whole-cell recordings from mPFC layer V pyramidal neurons revealed that U69,593 decreased the frequency, but not amplitude, of glutamatergic mini EPSPs. To determine whether KOR regulation of mPFC DA overflow was mediated by KOR on DA terminals, we utilized a Cre recombinase-driven mouse line lacking KOR in DA neurons. In these mice, basal DA release or uptake was unaltered relative to controls, but attenuation of mPFC DA overflow by local U69,593 was not observed, indicating KOR acts directly on mPFC DA terminals to locally inhibit DA levels. Conditioning procedures were then used to determine whether mPFC KOR signaling was necessary for KOR-mediated aversion. U69,593-mediated conditioned place aversion was blocked by intra-mPFC nor-BNI microinjection. These findings demonstrate that mPFC KORs negatively regulate DA and amino-acid neurotransmission, and are necessary for KOR-mediated aversion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prefrontal Cortical Kappa Opioid Receptors Attenuate Responses to Amygdala Inputs.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 Dec;40(13):2856-64. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.138. Epub 2015 May 14. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25971593 Free PMC article.
-
Kappa opioid receptors on dopaminergic neurons are necessary for kappa-mediated place aversion.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Dec;38(13):2623-31. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.171. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23921954 Free PMC article.
-
Age-dependent regulation of GABA transmission by kappa opioid receptors in the basolateral amygdala of Sprague-Dawley rats.Neuropharmacology. 2017 May 1;117:124-133. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.01.036. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28163104 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling monoamine receptors involved in the action of typical and atypical antipsychotics on glutamatergic and serotonergic transmission in prefrontal cortex.Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(5):502-15. doi: 10.2174/138161210790361416. Curr Pharm Des. 2010. PMID: 19909228 Review.
-
Dynorphin, stress, and depression.Brain Res. 2010 Feb 16;1314:56-73. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.09.074. Epub 2009 Sep 24. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 19782055 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neurokinin-1 Antagonism Distinguishes the Role of Norepinephrine Transporter from Dopamine Transporter in Mediating Amphetamine Behaviors.Pharmacology. 2021;106(11-12):597-605. doi: 10.1159/000518033. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Pharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34515205 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of kappa opioid receptor neuromodulation of lateral habenula synaptic function following a repetitive mild traumatic brain injury.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2024 Oct;243:173838. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2024.173838. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2024. PMID: 39067532
-
Selective kappa-opioid antagonism ameliorates anhedonic behavior: evidence from the Fast-fail Trial in Mood and Anxiety Spectrum Disorders (FAST-MAS).Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020 Sep;45(10):1656-1663. doi: 10.1038/s41386-020-0738-4. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32544925 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic stimulation of dynorphinergic neurons within the dorsal raphe activate kappa opioid receptors in the ventral tegmental area and ablation of dorsal raphe prodynorphin or kappa receptors in dopamine neurons blocks stress potentiation of cocaine reward.Addict Neurosci. 2022 Mar;1:100005. doi: 10.1016/j.addicn.2022.100005. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Addict Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36176476 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of biased signaling at the kappa opioid receptor.Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 11;14(1):1338. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37041-7. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36906681 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Backman CM, Malik N, Zhang Y, Shan L, Grinberg A, Hoffer BJ, et al. Characterization of a mouse strain expressing Cre recombinase from the 3′ untranslated region of the dopamine transporter locus. Genesis. 2006;44:383–390. - PubMed
-
- Bals-Kubik R, Ableitner A, Herz A, Shippenberg TS. Neuroanatomical sites mediating the motivational effects of opioids as mapped by the conditioned place preference paradigm in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;264:489–495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

