Targeting oncogenic ALK and MET: a promising therapeutic strategy for glioblastoma
- PMID: 23543207
- PMCID: PMC4314306
- DOI: 10.1007/s11011-013-9401-7
Targeting oncogenic ALK and MET: a promising therapeutic strategy for glioblastoma
Abstract
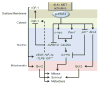
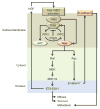
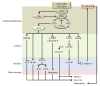
Glioblastoma is the most common aggressive, highly glycolytic, and lethal brain tumor. In fact, it is among the most commonly diagnosed lethal malignancies, with thousands of new cases reported in the United States each year. Glioblastoma's lethality is derived from a number of factors including highly active pro-mitotic and pro-metastatic pathways. Two factors increasingly associated with the intracellular signaling and transcriptional machinery required for such changes are anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and the hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGFR or, more commonly MET). Both receptors are members of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family, which has itself gained much attention for its role in modulating mitosis, migration, and survival in cancer cells. ALK was first described as a vital oncogene in lymphoma studies, but it has since been connected to many carcinomas, including non-small cell lung cancer and glioblastoma. As the receptor for HGF, MET has also been highly characterized and regulates numerous developmental and wound healing events which, when upregulated in cancer, can promote tumor progression. The wealth of information gathered over the last 30 years regarding these RTKs suggests three downstream cascades that depend upon activation of STAT3, Ras, and AKT. This review outlines the significance of ALK and MET as they relate to glioblastoma, explores the significance of STAT3, Ras, and AKT downstream of ALK/MET, and touches on the potential for new chemotherapeutics targeting ALK and MET to improve glioblastoma patient prognosis.
Figures

References
-
- Aaronson DS, Horvath CM. A road map for those who don't know JAK-STAT. Science. 2002;296:1653–1655. - PubMed
-
- Anandharaj A, Cinghu S, Park WY. Rapamycin-mediated mTOR inhibition attenuates survivin and sensitizes glioblastoma cells to radiation therapy. Acta biochimica et biophysica Sinica. 2011;43:292–300. - PubMed
-
- Arrieta O, Garcia E, Guevara P, Garcia-Navarrete R, Ondarza R, Rembao D, Sotelo J. Hepatocyte growth factor is associated with poor prognosis of malignant gliomas and is a predictor for recurrence of meningioma. Cancer. 2002;94:3210–3218. - PubMed
-
- Bajbouj K, Mawrin C, Hartig R, Schulze-Luehrmann J, Wilisch-Neumann A, Roessner A, Schneider-Stock R. P53-dependent antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic effects of trichostatin A (TSA) in glioblastoma cells. Journal of neuro-oncology. 2012;107:503–516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

