Parenting interventions for the prevention of unintentional injuries in childhood
- PMID: 23543542
- PMCID: PMC8908963
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006020.pub3
Parenting interventions for the prevention of unintentional injuries in childhood
Abstract
Background: Parent education and training programmes can improve maternal psychosocial health, child behavioural problems and parenting practices. This review assesses the effects of parenting interventions for reducing child injury.
Objectives: To assess the effects of parenting interventions for preventing unintentional injury in children aged under 18 years and for increasing possession and use of safety equipment and safety practices by parents.
Search methods: We searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE, EMBASE, BIOSIS Preview, PsycINFO, Sociological Abstracts, Social Science Citation Index, CINAHL, ProQuest Dissertations and Theses, ERIC, DARE, ASSIA, Web of Science, SIGLE and ZETOC. We also handsearched abstracts from the World Conferences on Injury Prevention & Control and the journal Injury Prevention. The searches were conducted in January 2011.
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled trials (RCTs), non-randomised controlled trials (non-RCTs) and controlled before and after studies (CBAs), which evaluated parenting interventions administered to parents of children aged 18 years and under, and reported outcome data on injuries for children (unintentional or unspecified intent), possession and use of safety equipment or safety practices (including the Home Observation for Measurement of the Environment (HOME) scale which contained an assessment of home safety) by parents. Parenting interventions were defined as those with a specified protocol, manual or curriculum aimed at changing knowledge, attitudes or skills covering a range of parenting topics.
Data collection and analysis: Studies were selected, data were extracted and quality appraised independently by two authors. Pooled relative risks (RR) were estimated using random effect models.
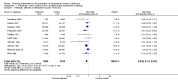
Main results: Twenty two studies were included in the review: 16 RCTs, two non-RCTs, one partially randomised trial which contained two randomised intervention arms and one non-randomised control arm, two CBA studies and one quasi randomised controlled trial. Seventeen studies provided interventions comprising parenting education and other support services; 15 of which were home visiting programmes and two of which were paediatric practice-based interventions. Two provided solely educational interventions. Nineteen studies recruited families who were from socio-economically disadvantaged populations, were at risk of adverse child outcomes or people who may benefit from extra support, such as single mothers, teenage mothers, first time mothers and mothers with learning difficulties. Ten RCTs involving 5074 participants were included in the meta-analysis, which indicated that intervention families had a statistically significant lower risk of injury than control families (RR 0.83, 95% CI 0.73 to 0.94). Sensitivity analyses undertaken including only RCTs at low risk of various sources of bias found the findings to be robust to including only those studies at low risk of detection bias in terms of blinded outcome assessment and attrition bias in terms of follow up of fewer than 80% of participants in each arm. When analyses were restricted to studies at low risk of selection bias in terms of inadequate allocation concealment the effect size was no longer statistically significant. Several studies found statistically significant fewer home hazards or a greater number of safety practices in intervention families. Of ten studies reporting scores on the HOME scale, data from three RCTs were included in a meta-analysis which found no evidence of a difference in quality of the home environment between treatment arms (mean difference 0.57, 95% CI -0.59 to 1.72). Most of the studies reporting home safety practices, home hazards or composite home safety scores found statistically significant effects favouring intervention arm families. Overall, using GRADE, the quality of the evidence was rated as moderate.
Authors' conclusions: Parenting interventions, most commonly provided within the home using multi-faceted interventions are effective in reducing child injury. There is fairly consistent evidence that they also improve home safety. The evidence relates mainly to interventions provided to families from disadvantaged populations, who are at risk of adverse child health outcomes or whose families may benefit from extra support. Further research is required to explore mechanisms by which these interventions may reduce injury, the features of parenting interventions that are necessary or sufficient to reduce injury and the generalisability to different population groups.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures




Update of
-
Parenting interventions for the prevention of unintentional injuries in childhood.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Oct 17;(4):CD006020. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006020.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Mar 28;(3):CD006020. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006020.pub3. PMID: 17943875 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Armstrong 2000 {published data only}
-
- Armstrong KL, Fraser JA, Dadds MR, Morris J. Promoting a secure attachment, maternal mood and child health in a vulnerable population: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2000;36:555‐62. - PubMed
Barlow 2007 {published data only}
-
- Barlow J, Davis H, McIntosch E, Jarrett P, Mockford C, Stewart‐Brown S. Role of home visiting in improving parenting and health in families at risk of abuse and neglect: results of a multicentre randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2007;92(3):229‐33. - PMC - PubMed
Caldera 2007 {published data only}
-
- Caldera D, Burrell L, Rodriguez K, Crowne SS, Rodhe C, Duggan A. Impact of a statewide home visiting program on parenting and on child health and development. Child Abuse & Neglect 2007;31:829‐52. - PubMed
Culp 2007 {unpublished data only}
-
- Culp AM, Culp R, Anderson J, Carter S. Health and safety intervention with first‐time mothers. Health Education Research 2007;22(2):285‐94. - PubMed
Duggan 1999 {published data only}
-
- Duggan AK, McFarlane EC, Windham AM, Rhode CA, Salkever DS, Fuddy L, et al. Evaluation of Hawaii's Healthy Start Program. Future of Children 1999;9(1):66‐90. - PubMed
Emond 2002 {published data only}
Feldman 1992 {published data only}
-
- Feldman MA, Case L, Sparks B. Effectiveness of a child‐care training program for parents at‐risk for child neglect. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science 1992;24(1):14‐28.
Fergusson 2005 {published data only}
-
- Fergusson DM, Grant H, Horwood LJ, Ridder EM. Randomized trial of the early start program of home visitation. Pediatrics 2005;116:803‐9. - PubMed
Gutelius 1977 {published data only}
-
- Gutelius MF, Kirsch AD, McDonald S, Riddick Brooks M, McErlan T. Controlled study of child health supervision: behaviour results. Pediatrics 1977;60(3):294‐304. - PubMed
Hardy 1989 {published data only}
-
- Hardy JB, Streett R. Family support and parenting education in the home: an effective extension of clinic‐based preventive health care services for poor children. Journal of Pediatrics 1989;115(6):927‐31. - PubMed
IHDP 1990 {published data only}
-
- The Infant Health & Development Program. Enhancing the outcomes of low‐birth‐weight, premature infants. A multisite, randomized trial. Journal of the American Medical Association 1990;263(22):3035‐42. - PubMed
Johnson 1993 {published data only}
Johnston 2004 {published data only}
-
- Johnston B, Huebner CE, Tyll LT, Barlow WE, Thompson RS. Expanding developmental and behavioural services for newborns in primary care: effects on parental well being, practice and satisfaction. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2004;26(4):356‐66. - PubMed
Kemp 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kemp L, Harris E, McMahon C, Matthey S, Vimpani G, Anderson T, et al. Child and family outcomes of a long‐term nurse home visitation programme: a randomised controlled trial. Archives of Diseases in Childhood 2011;96:533‐540. - PubMed
Kitzman 1997 {published data only}
-
- Kitzman H, Olds DL, Henderson CR, Hanks C, Cole R, Tatelbaum R, et al. Effect of prenatal and infancy home visitation by nurses on pregnancy outcomes, childhood injuries, and repeated childbearing. A randomised controlled trial. Journal of the American Medical Association 1997;278(8):644‐52. - PubMed
Koniak‐Griffin 2003 {published data only}
-
- Koniak‐Griffin D, Verzemnieks IL, Anderson NLR, Brecht M‐L, Lesser J, Kim S, et al. Nurse visitation for adolescent mothers. Nursing Research 2003;52(2):127‐136. - PubMed
Larson 1980 {published data only}
-
- Larson CP. Efficacy of prenatal and postpartum home visits on child health and development. Pediatrics 1980;66(2):191‐7. - PubMed
Llewellyn 2003 {published data only}
-
- Llewellyn G, McConnell D, Honey A, Mayes R, Russo D. Promoting health and home safety for children of parents with intellectual disability: a randomized controlled trial. Research in Developmental Disabilities 2003;24(6):405‐31. - PubMed
Minkovitz 2003 (a) {published data only}
-
- Minkovitz C, Hughart N, Strobino D, Scharfstein D, Grason H, Hou W, et al. A practice‐based intervention to enhance quality of care in the first 3 years of life. Journal of the American Medical Association 2003;293(23):3081‐91. - PubMed
Minkovitz 2003 (b) {published data only}
-
- Minkovitz C, Hughart N, Strobino D, Scharfstein D, Grason H, Hou W, et al. A practice‐based intervention to enhance quality of care in the first 3 years of life. Journal of the American Medical Association 2003;293(23):3081‐91. - PubMed
Olds 1986 {published data only}
-
- Olds DL, Henderson CR, Chamberlain R Jr, Tatelbaum R. Preventing child abuse and neglect: a randomized trial of nurse home visitation. Pediatrics 1986;78(1):65‐78. - PubMed
St Pierre 1999 {published data only}
-
- Pierre R, Layzer JI. Using home visits for multiple purposes: the Comprehensive Child Development Program. The Future of Children 1999;1:134‐151. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Akinbami 2001 {published data only}
-
- Akinbami LJ, Cheng TL, Kornfeld D. A review of teen‐tot programs: comprehensive clinical care for young parents and their children. Adolescence 2001;36(142):381‐93. - PubMed
Babul 2007 {published data only}
-
- Babul S, Olsen L, Janseen P, McIntee P, Raina P. A randomized trial to access the effectiveness of an infant home safety programme. International Journal of Injury Control and Safety Promotion 2007;14(2):109‐17. - PubMed
Baron‐Epel 2006 {published data only}
-
- Baron‐Epel O, Hemmo‐Lotem M, Mike‐Doron R, Endy‐Findling L, Balin L. Injury prevention counselling of families with children hospitalized due to injuries: the "Personalized Injury Prevention" program. 8th World Conference on Injury Prevention and Safety Promotion. South Africa, 2006.
Beirens 2006 {published data only}
-
- Beirens T. Effectiveness of standardized safety information provided through Dutch well‐child clinics to parents of 11‐18 months old toddlers. World Safety Conference. 2006.
Bond 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bond LA, Burns CE. Mothers' beliefs about knowledge, child development and parenting strategies: expanding the goals of parenting programs. The Journal of Primary Prevention 2006;27(6):555‐71. - PubMed
Conroy 1994 {published data only}
-
- Conroy M. Increasing agreement on safe parenting in two‐parent families at risk for physical child abuse (Dissertation). University of San Francisco 1994.
Culp 1998 {published data only}
-
- Culp AM, Culp RE, Blankmeyer M, Passmark L. Parent education home visitation program: adolescent and non adolescent mother comparison after 6 months of intervention. Infant Mental Health Journal 1998;19(2):111‐23. - PubMed
Cupples 2011 {published data only}
-
- Cupples ME, Stewart MC, Percy A, Hepper P, Murphy C, Halliday HL. A RCT of peer‐mentoring for first‐time mothers in socially disadvantaged areas (the MOMENT study). Archives of Diseases in Childhood 2011;96:252‐8. - PubMed
Dawson 1989 {published data only}
-
- Dawson P, Doorninck WJ, Robinson JL. Effects of home based, informal social support on child health. Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics 1989;10(2):63‐7. - PubMed
Donnellan 1981 {published data only}
-
- Donnellan GJ, et al. Prevention Service programs for infants of mentally‐ill mothers: progress report. 89th Annual Meeting of the.American Psychological Association. Los Angeles, CA, August 24‐28, 1981.
Ertem 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ertem IO, Atay G, Bingoler BE, Dogan DG, Bayhan A, Sarica D. Promoting child development at sick‐child visits: a controlled trial. Pediatrics 2006;118(1):124‐31. - PubMed
Feldman 2004 {published data only}
-
- Feldman MA. Self‐directed learning of child‐care skills by parents with intellectual disabilities. Infants and Young Children 2004;17(1):17‐31.
Fitzpatrick 1997 {published data only}
Gershater‐Molko 2002 {published data only}
-
- Gershater Molko RM, Lutzker JR, Wesch D. Project SafeCare: improving health, safety, and parenting skills in families reported for, and at‐risk for, child maltreatment. Journal of Family Violence 2003;18(6):377‐86.
Gershater‐Molko 2003 {published data only}
-
- Gershater‐Molko RM. A comprehensive evaluation of project Safecare: health, safety, bonding and recidivism in families reported for, and at risk for, child maltreatment, and finishing treatment (Dissertation). University of Kansas 2002.
Gray 1979 {published data only}
-
- Gray JD, Cutler CA, Dean JG, Kempe CH. Prediction and prevention of child abuse and neglect. Journal of Social Issues 1979;35(2):127‐39. - PubMed
Guyer 2000 {published data only}
-
- Guyer B, Hughart N, Strobino D, Jones A, Scharfstein D. Assessing the impact of pediatric‐based developmental services on infants, families and clinicians: challenges to evaluating the Healthy Steps Program. Pediatrics 2000;105(3):E33. - PubMed
Hedges 2005 {published data only}
-
- Hedges S, Simmes D, Martinez A, Linder C, Brown S. A home visitation program welcomes home first‐time moms and their infants. Home Healthcare Nurse 2005;23(5):286‐9. - PubMed
Hemmo‐Lotom 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hemmo‐Lotom, M. Parental knowledge, attitudes and practice concerning prevention of children's falls. 8th World Conference on Injury Prevention and Safety Promotion. South Africa, 2006.
Huxley 1993 {published data only}
-
- Huxley P, Warner R. Primary prevention of parenting dysfunction in high‐risk cases. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry 1993;63(4):582‐8. - PubMed
Jackson 2009 {published data only}
Johnson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Johnson S, Whitelaw A, Glazebrook C, Israel C, Turner R, White IR, et al. Randomized trial of a parenting intervention for very preterm infants: outcome at 2 years. The Journal of Pediatrics 2009;155(4):488‐94. - PubMed
Jordaan 2006 {published data only}
-
- Jordaan E. The usefulness of a new instrument, developed to measure the prevention effect of the home visitation programme, focussing on unintentional home injuries in young children in a low income South African setting. 8th World Conference on Injury Prevention and Safety Promotion, South Africa. 2006.
Jouriles 2010 {published data only}
-
- Jouriles EN, McDonald R, Rosenfiled D, Norwood WD, Spiller L, Stephens N, et al. Improving parenting in families referred for child maltreatment: a randomized controlled trial examining effects of project support. Journal of Family Psychology 2010;24(3):328‐38. - PubMed
Kluger 2000 {published data only}
-
- Kluger MP, Alexander G, Curtis PA (editors). What Works in Child Welfare. CWLA, USA, 2000.
Lealman 1983 {published data only}
-
- Lealman GT, Haigh D, Phillips JM, Stone J, Ord‐Smith C. Prediction and prevention of child abuse ‐ an empty hope. The Lancet 1983;1(8339):1423‐4. - PubMed
McAuley 2004 {published data only}
-
- McAuley C, Knapp M, Beecham J, McCurry N, Sleed M. Young families under stress. Outcomes and costs of home start support. York, Joseph Rowntree Foundation, 2004.
Odendall 2009 {published data only}
-
- Odendall W. The impact of a home visitation programme on household hazards associated with unintentional childhood injuries: a randomised controlled trial. Accident Analysis and Prevention 2009;41(1):182‐90. - PubMed
Powell 2004 {published data only}
Quraishi 2005 {published data only}
-
- Quraishi AY, Mickalide AD, Cody BE. Follow the leader: a national study of safety role modelling among parents and children. Washington, DC, National SAFE KIDS Campaign, April 2005.
Sharma 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sharma G. Educational intervention in changing knowledge of mothers of under five children in reducing injuries among Nepalese children. 8th World Conference on Injury Prevention and Safety Promotion, South Africa. 2006.
Smith 1984 {published data only}
-
- Smith JE, Rachman SJ. Non‐accidental injury to children‐II. A controlled evaluation of a behavioural management programme. Behaviour Research and Therapy 1984;22(4):349‐66. - PubMed
Subhi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Subhi B. Community orientation and promotion and home injuries prevention among Arab children in Israel. BASPCAN Seventh National Congress, Swansea. 2009.
Swart 2008 {published data only}
-
- Swart L, Niekerk A, Seedat M, Jorddann E. Paraprofessional home visitation program to prevent childhood unintentional injuries in low‐income communities: a cluster randomized controlled trial. Injury Prevention 2008;14(3):164‐9. - PubMed
Taban 2001 {published data only}
-
- Taban N, Lutzker JR. Consumer evaluation of an ecobehavioural program for prevention and intervention of child maltreatment. Journal of Family Violence 2001;16(3):323‐30.
Trudeau 2010 {published data only}
-
- Trudeau J, Stephens Stidhams S, Istre GR, Weir C, Johnson U. Using lay home educators to provide safety messages in Dallas, TX, USA. 10th World Conference on Injury Prevention and Safety Promotion, London. 2010.
Tsoumakas 2009 {published data only}
-
- Tsoumakas K, Dousis E, Mavridi F, Gremou A, Matziou V. Parent's adherence to children's home‐accident preventive measures. International Nursing Review 2009;56(3):369‐74. - PubMed
Van As, 2006 {published data only}
-
- As A. Creating a safer environment for children: the need for an integrative family approach. In: 8th World Conference on Injury Prevention and Safety Promotion, South Africa. 2006.
Additional references
Barlow 2000
-
- Barlow J, Stewart‐Brown S. Behavior problems and group‐based parent education programs. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics 2000;21(5):356‐70. - PubMed
Barlow 2002
Barlow 2003
Barlow 2006
Barlow 2008
-
- Barlow J, Davis H, McIntosh E, Kirkpatrick E, Peters R, Jarrett P, et al. The Oxfordshire Home Visiting study. Unpublished report 2008.
Beautrais 1981
-
- Beautrais AL, Fergusson DM, Shannon FT. Accidental poisoning in the first three years of life. Australian Paediatric Journal 1981;17(2):104‐9. - PubMed
Beautrais 1982
-
- Beautrais AL, Fergusson DM, Shannon FT. Life events and childhood morbidity: a prospective study. Pediatrics 1982;70(6):935‐40. - PubMed
Bijur 1986
-
- Bijur PE, Stewart‐Brown S, Butler N. Child behavior and accidental injury in 11,966 preschool children. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1986;140(5):487‐92. - PubMed
Bijur 1988a
-
- Bijur P, Golding J, Haslum M, Kurzon M. Behavioral predictors of injury in school‐age children. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1988;142(12):1307‐12. - PubMed
Bijur 1988b
-
- Bijur PE, Golding J, Haslum M. Persistence of occurrence of injury: can injuries of preschool children predict injuries of school‐aged children?. Pediatrics 1988;82(5):707‐12. - PubMed
Bradbury 1999
-
- Bradbury K, Janicke DM, Riley AW, Finney JW. Predictors of unintentional injuries to school‐age children seen in pediatric primary care. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1999;24(5):423‐33. - PubMed
Brown 1978
-
- Brown GW, Davidson S. Social class, psychiatric disorder of mother, and accidents to children. Lancet 1978;1(8060):378‐81. - PubMed
Bussing 1996
-
- Bussing R, Menvielle E, Zima B. Relationship between behavioral problems and unintentional injuries in US children. Findings of the 1988 National Health Interview Survey. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 1996;150(1):50‐6. - PubMed
Caldwell 2003
-
- Caldwell BM, Bradley RH. Home Observation for Measurement of the Environment. Administration manual. Tempe, AZ, Family & Human Dynamics Research Institute, Arizona State University, 2003.
Coren 2002
-
- Coren E, Barlow J, Stewart‐Brown S. Systematic review of the effectiveness of parenting programmes for teenage parents. Journal of Adolescence 2002;26(1):79‐103. - PubMed
DTI 2003
-
- Department of Trade and Industry. 24th (final) report of the Home and Leisure Accident Surveilance System ‐ 2000, 2001, 2002 data. London, Department of Trade and Industry, 2003.
Duggan 2004
-
- Duggan A, McFarlane E, Fuddy L, Burrell L, Higman SM, Windham A, et al. Randomized trial of a statewide home visiting program: impact in preventing child abuse and neglect. Child Abuse and Neglect 2004;28:597‐622. - PubMed
Duggan 2007
-
- Duggan A, Caldera D, Rodriguez K, Burrell L, Rohde C, Crowne SS. Impact of a statewide home visiting program to prevent child abuse. Child Abuse and Neglect 2007;31:801‐27. - PubMed
Edwards 2006
Elkan 2000
-
- Elkan R, Kendrick D, Hewitt M, Robinson JJ, Tolley K, Blair M, et al. The effectiveness of domiciliary health visiting: a systematic review of international studies and a selective review of the British literature. Health Technology Assessment 2000;4(13):1‐339. - PubMed
Fraser 2000
-
- Fraser JA, Armstrong KL, Morris JP, Dadds MR. Home visiting intervention for vulnerable families with newborns: follow‐up results of a randomized controlled trial. Child Abuse and Neglect 2000;24(11):1399‐429. - PubMed
Goodson 2000
-
- Goodson BD, Layzer JI, St. Pierre RG, Bernstein L, Lopez M. Effectiveness of a comprehensive, five‐year family support program for low‐income children and their families: findings from the Comprehensive Child Development Program. Early Childhood Research Quarterly 2000;15(1):5‐39.
Harris 1994
-
- Harris MJ, Kotch JB. Unintentional infant injuries: sociodemographic and psychosocial factors. Public Health Nursing 1994;11(2):90‐7. - PubMed
Higgins 2005
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 4.2.5 [updated May 2005]. http://www.cochrane.org/resources/handbook/hbook.htm.
Hippisley‐Cox 2002
Hunt 2003
-
- Hunt C. The parenting puzzle ‐ how to get the best out of family life. The parenting puzzle ‐ how to get the best out of family life. Oxford, Family Links, 2003.
Johnson 2000
-
- Johnson Z, Molloy B, Scallan E, Fitzpatrick P, Rooney B, Keegan T, et al. Community Mothers programme ‐ seven year follow‐up of a randomized controlled trial of non‐professional intervention in parenting. Journal of Public Health Medicine 2000;22(3):337‐42. - PubMed
Johnston 2006
-
- Johnston BD, Huebner CE, Anderson ML, Tyll LT, Thompson RS. Healthy Steps in an integrated delivery system. Child and parent outcomes at 30 months. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine 2006;160:793‐800. - PubMed
Kemp 2008
Kendrick 1999
Kendrick 2000
Kendrick 2012
Lam 2005
-
- Lam LT. Attention deficit disorder and hospitalisation owing to intra‐ and interpersonal violence among children and young adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health 2005;36(1):19‐24. - PubMed
McLennan 2000
-
- McLennan JD, Kotelchuck M. Parental prevention practices for young children in the context of maternal depression. Pediatrics 2000;105(5):1090‐5. - PubMed
Miller 2004
-
- Miller AR, Brehaut JC, Raina P, McGrail KN, Armstrong RW. Use of medical services by methlyphenidate‐treated children in the general population. Ambulatory Pediatrics 2004;4(2):174‐80. - PubMed
O'Connor 2000
-
- O'Connor TG, Davies L, Dunn J, Golding J. Distribution of accidents, injuries, and illnesses by family type. ALSPAC Study Team. Avon Longitudinal Study of Pregnancy and Childhood. Pediatrics 2000;106(5):E68. - PubMed
Olds 1994
-
- Olds DL, Henderson Jr CR, Kitzman H. Does prenatal and infancy nurse home visitation have enduring effects on qualities of parental caregiving and child health at 25 to 50 months of life?. Pediatrics 1994;93(1):89‐98. - PubMed
ONS 2009
-
- Office for National Statistics. Mortality statistics: deaths registered in 2008 DDRR__0078. Review of the National Statistician on Deaths in England and Wales, 2008. London, Office for National Statistics, 2009. http://www.statistics.gov.uk/downloads/theme_health/DR2008/DR_08.pdf. (accessed 12 September 2010). London, Office for National Statistics, 2009..
Roberts 1996
Roberts 1996b
Roberts 1997
Rowe 2004
-
- Rowe R, Maughan B, Goodman R. Childhood psychiatric disorder and unintentional injury: findings from a national cohort study. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2004;29(2):119‐30. - PubMed
Sanders 2002
-
- Sanders M, Markie‐Dadds C, Turner KMT, Brechman‐Toussaint M. Triple P: A guide to the system. Queensland, Triple P International, 2002.
Schwebel 2004
-
- Schwebel DC, Brezausek CM, Ramey SL, Ramey CT. Interactions between child behavior patterns and parenting: implications for children's unintentional injury risk. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2004;29:93‐104. - PubMed
Smithson 2011
Soubhi 2004
-
- Soubhi H. The social context of childhood injury in Canada: integration of the NLSCY findings. American Journal of Health Behavior 2004;28 Suppl 1:S38‐S50. - PubMed
The NHS Information Centre 2007
-
- The NHS Information Centre. Hospital Episode Statistics (HES), 2007. www.hesonline.nhs.uk (accessed 12 September 2010).
Totsika 2004
-
- Totsika V, Sylva K. The Home Observation for Measurement of the Environment Revisited. Child and Adolescent Mental Health 2004;9(1):25‐35. - PubMed
UNICEF 2001
-
- UNICEF. A league table of child deaths by injury in rich nations. Innocenti Report Card Issue no. 2. Florence, UNICEF Innocenti Research Centre, February 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

