Educational games for health professionals
- PMID: 23543543
- PMCID: PMC7389433
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006411.pub4
Educational games for health professionals
Abstract
Background: The use of games as an educational strategy has the potential to improve health professionals' performance (e.g. adherence to standards of care) through improving their knowledge, skills and attitudes.
Objectives: The objective was to assess the effect of educational games on health professionals' performance, knowledge, skills, attitude and satisfaction, and on patient outcomes.
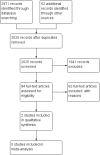
Search methods: We searched the following databases in January 2012: MEDLINE, AMED, CINAHL, Cochrane Central Database of Controlled Trials, EMBASE, EPOC Register, ERIC, Proquest Dissertations & Theses Database, and PsycINFO. Related reviews were sought in DARE and the above named databases. Database searches identified 1546 citations. We also screened the reference lists of included studies in relevant reviews, contacted authors of relevant papers and reviews, and searched ISI Web of Science for papers citing studies included in the review. These search methods identified an additional 62 unique citations for a total of 1608 for this update.
Selection criteria: We included randomized controlled trials (RCT), controlled clinical trials (CCT), controlled before and after (CBA) and interrupted time-series analysis (ITS). Study participants were qualified health professionals or in postgraduate training. The intervention was an educational game with "a form of competitive activity or sport played according to rules".
Data collection and analysis: Using a standardized data form we extracted data on methodological quality, participants, interventions and outcomes of interest that included patient outcomes, professional behavior (process of care outcomes), and professional's knowledge, skills, attitude and satisfaction.
Main results: The search strategy identified a total of 2079 unique citations. Out of 84 potentially eligible citations, we included two RCTs. The game evaluated in the first study used as a reinforcement technique, was based on the television game show "Family Feud" and focused on infection control. The study did not assess any patient or process of care outcomes. The group that was randomized to the game had statistically higher scores on the knowledge test (P = 0.02). The second study compared game-based learning ("Snakes and Ladders" board game) with traditional case-based learning of stroke prevention and management. The effect on knowledge was not statistically different between the two groups immediately and 3 months after the intervention. The level of reported enjoyment was higher in the game-based group.
Authors' conclusions: The findings of this systematic review neither confirm nor refute the utility of games as a teaching strategy for health professionals. There is a need for additional high-quality research to explore the impact of educational games on patient and performance outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Three of the authors were involved in developing games for medical education (EAA, HJS).
Update of
-
Educational games for health professionals.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jan 31;(1):CD006411. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006411.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Mar 28;(3):CD006411. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006411.pub4. PMID: 23440807 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Burke 2001 {published data only}
-
- Burke CT. The influences of teaching strategies and reinforcement techniques on health care workers' learning and retention [PhD thesis]. Hattiesburg: University of Southern Mississippi, 2001. [UMI Microform 3038675]
Telner 2010 {published data only}
References to studies excluded from this review
Akl 2008a {published data only}
Akl 2010 {published data only}
Amos1994 {published data only}
-
- Amos A. Annual recertification: fun? Wow!. CANNT journal : the journal of the Canadian Association of Nephrology Nurses and Technicians 1994;4(1):21‐4. - PubMed
Andrade 2008 {published data only}
-
- Andrade, R. Educational games: training of community healthcare agents on children's respiratory diseases. Acta Paulista de Enfermagem 2008;21(3):444‐448.
Backstein 2010 {published data only}
-
- Backstein D, Cowan B, Cristancho S, Dubrowski A, Kapralos B, Porte M, et al. A serious game for total knee arthroplasty procedure, education and training. Journal of Cyber Therapy and Rehabilitation 2010;3(3):285‐98.
Barber‐Madden1989 {published data only}
-
- Barber‐Madden R, Glanz K. Participatory learning in continuing nursing education: Soviet edition of a public health and medicine trivia game. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 1989;20(3):128‐31. - PubMed
Bauman 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bauman, E. Games and simulation in healthcare: past, present, and future ‐‐ an expert panel. Clinical Simulation in Nursing 2010;6(3):e108.
Begg 2008 {published data only}
-
- Begg M. Leveraging game‐informed healthcare education. Medical Teacher 2008;30(2):155‐8. - PubMed
Bergeron 2008 {published data only}
-
- Bergeron BP. Learning & retention in adaptive serious games. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics 2008;132:26‐30. [PUBMED: 18391250] - PubMed
Bhoopathi 2006 {published data only}
Bhoopathi 2007 {published data only}
-
- Bhoopathi PS, Sheoran R, Adams CE. Educational games for mental health professionals: a Cochrane review. The International Journal of Psychiatric Nursing Research 2007;12(3):1497‐502. - PubMed
Boreham 1989 {published data only}
-
- Boreham N, Foster R, Mawer G. The phenytoin game: its effect on decision skills. Simulation & Games 1989;20(3):292‐9. [DOI: 10.1177/104687818902000304] - DOI
Boulet 2007 {published data only}
Brinson 1988 {published data only}
-
- Brinson SATB. A comparison of two teaching methods: a game and a lecture to review mandatory workplace safety in acute care hospitals [PhD thesis]. San Diego: United States International University, 1988.
Burns 1984 {published data only}
-
- Burns KA. Experience in the use of gaming and simulation as an evaluation tool for nurses. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 1984;15(6):213‐7. - PubMed
Carlson 1992 {published data only}
-
- Carlson DS, Colvin MK. Making a challenge out of an NLN visit: any more questions?. Nurse Educator 1992;17(4):27‐9. - PubMed
Cessario 1987 {published data only}
-
- Cessario L. Utilization of board gaming for conceptual models of nursing. The Journal of Nursing Education 1987;26(4):167‐9. - PubMed
Christmas 2007 {published data only}
-
- Christmas C, Ziegelstein RC. Systems survivor: voting unsafe patient care practices off the island. Teaching and Learning in Medicine 2007;19(2):200‐1. - PubMed
Cowen 2002 {published data only}
-
- Cowen KJ, Tesh AS. Effects of gaming on nursing students' knowledge of pediatric cardiovascular dysfunction. The Journal of Nursing Education 2002;41(11):507‐9. - PubMed
D'Alessandro 2002 {published data only}
-
- D'Alessandro DM, Ellsbury DL, Kreiter CD, Starner T. Pediatric jeopardy may increase residents' medical reading. Ambulatory Pediatrics 2002;2(1):1‐3. - PubMed
Dowd 2003 {published data only}
-
- Dowd SB, Root A. The hospital manager and game theory: chess master, poker player, or cooperative game player?. Health Care Manager 2003;22(4):305‐10. - PubMed
Dowd 2004 {published data only}
-
- Dowd SB. Applied game theory for the hospital manager: three case studies. Health Care Manager 2004;23(2):156‐61. - PubMed
Durman 2002 {published data only}
-
- Durman S, Dias DC, Stefanelli MC. Validation of an educational game for therapeutic comunication [sic] discussion [Portuguese]. Revista Eletrônica de Enfermagem 2002;4(2):10‐3.
Espinosa 2006 {published data only}
-
- Espinosa C, Viladrich M. Computer professionals and nurses: growing together. International Journal of Nursing Terminologies and Classifications 2006;17(1):69‐70.
Feldman 1985 {published data only}
-
- Feldman HR. The organization game. Nursing Management 1985;16(9):47‐9. - PubMed
Finn 2011 {published data only}
-
- Finn D, Nolley B, Young JS. Performance in 'war game' simulations between medical students and interns. The American Surgeon 2011;77(3):370‐2. - PubMed
Ford 1996 {published data only}
-
- Ford DA, Brown DM. You can be in Jeopardy. AORN Journal 1996;63(3):583‐7, 9. - PubMed
French 1980 {published data only}
-
- French P. Academic gaming in nurse education. Journal of Advanced Nursing 1980;5(6):601‐12. - PubMed
Gage 2011 {published data only}
-
- Gage M, Peckman GS, Greene MT. Using a "Survivor" style game to guide nursing research into practice. Journal of Hospital Librarianship 2011;11(1):94‐8.
Geyer1990 {published data only}
-
- Geyer KA, Korte PD. Creativity in nursing staff development. Journal for Nurses in Staff Development 1990;6(3):112‐7. - PubMed
Girardi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Girardi FM, Nieto FB, Vitoria LP, Borba Vieira PR, Guimaraes JB, Salvador S, et al. T‐ and B‐cell ontogeny: an alternative teaching method: T‐ and B‐cell ontogeny game. Teaching and Learning in Medicine 2006;18(3):251‐60. - PubMed
Gordon 1995 {published data only}
-
- Gordon DW, Brown HN. Fun and games in reviewing neonatal emergency care. Neonatal Network 1995;14(3):45‐9. - PubMed
Gruending 1991 {published data only}
-
- Gruending DL, Fenty D, Hogan T. Fun and games in nursing staff development. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 1991;22(6):259‐62. - PubMed
Guidry 2000 {published data only}
-
- Guidry JJ. Cultural sensitivity: BaFa BaFa cross‐cultural simulation exercise and its implications for rural health professionals. Texas Journal of Rural Health 2000;18(4):16‐21.
Hansen 2008 {published data only}
Harding 2001 {published data only}
-
- Harding SR, D'Eon MF. Using a Lego‐based communications simulation to introduce medical students to patient‐centered interviewing. Teaching and Learning in Medicine 2001;13(2):130‐5. - PubMed
Hodges 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hodges, P. "Management for $1000": an innovative teaching strategy. Communicating nursing research 2007;40:524.
Ingram 1998 {published data only}
-
- Ingram C, Ray K, Keane DR, Landeen J. Evaluation of an educational game for health sciences students. The Journal of Nursing Education 1998;37(6):240. - PubMed
Jirasevijinda 2010 {published data only}
-
- Jirasevijinda T, Brown LC. Jeopardy!: an innovative approach to teach psychosocial aspects of pediatrics. Patient Education and Counseling 2010;80(3):333‐6. - PubMed
Jones 2000 {published data only}
-
- Jones AG, Jasperson J, Gusa D. Cranial nerve wheel of competencies. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 2000;31(4):152‐4. - PubMed
Kurenov 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kurenov SN, Cance WW, Noel B, Mozingo DW. Game‐based mass casualty burn training. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics 2009;142:142‐4. - PubMed
LeCroy 2006 {published data only}
-
- LeCroy C. Games as an innovative teaching strategy for overactive bladder and BPH. Urologic Nursing 2006;26(5):381‐4, 93. - PubMed
Leidy 1992 {published data only}
-
- Leidy K. Enjoyable learning experiences‐‐an aid to retention?. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 1992;23(5):206‐8. - PubMed
Leonard 2008 {published data only}
-
- Leonard T, Westman D. Got Rhythm? Teaching the net generation. Critical Care Nurse 2008;28(2):e31.
Lim 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lim EC, Seet RC. Using an online neurological localisation game. Medical Education 2008;42(11):1117. - PubMed
Lopes 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lopes MVO, Araujo TL. Validation of the software "vital signs" for a panel of specialists [Portuguese]. Revista paulista de enfermagem 2003;22(2):166‐74.
Meidani 2006 {published data only}
-
- Meidani M, Kapadohos T. Using games as an alternative path of in‐service training. European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing 2006;5(Suppl 1):S31.
Meterissian 2007 {published data only}
-
- Meterissian S, Liberman M, McLeod P. Games as teaching tools in a surgical residency. Medical Teacher 2007;29(9):e258‐60. - PubMed
Montpas 2004 {published data only}
-
- Montpas MM. Comparison of "Jeopardy" game versus lecture on associate degree nursing students' achievement and retention of geriatric nursing concepts [PhD thesis]. Detroit, MI: Wayne State University, 2004. [Accession Number 2009014516]
Morton 2001 {published data only}
-
- Morton PG, Tarvin L. The Pain Game: pain assessment, management, and related JCAHO standards. Joint Commission on Accreditation of Health Care Organizations. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 2001;32(5):223‐7. [PUBMED: 11868739] - PubMed
O'Kane 1988 {published data only}
-
- O'Kane CS. 12 innovative teaching strategies for psychiatric nursing. AD Nurse 1988;3(1):13‐6. - PubMed
Ogershok 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ogershok PR, Cottrell S. The pediatric board game. Medical Teacher 2004;26(6):514‐7. - PubMed
Olbrich 1997 {published data only}
-
- Olbrich E. Teaching strategies. Innovative games for aide inservices. Home Care Manager 1997;1(1):18‐9, 26.
Parker 2005 {published data only}
Pearce‐Smith 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pearce‐Smith N. Teaching tip: using the "Who wants to be a millionaire?" game to teach searching skills. Evidence Based Nursing 2007;10(3):72. - PubMed
Petersen 2010 {published data only}
-
- Petersen M, Flavin B. Let the games begin. Journal of Emergency Nursing 2010;36(6):589‐90. - PubMed
Pittiglio 2011 {published data only}
-
- Pittiglio LI, Harris MA, Mili F. Development and evaluation of a three‐dimensional virtual hospital unit: VI‐MED. Computers, Informatics. Nursing 2011;29(5):267‐71. - PubMed
Pocock 1987 {published data only}
-
- Pocock P, Bellwood M, Payne B. Critical decisions... develop the learner nurse's understanding of mental health legislation. Senior Nurse 1987;6(6):26‐7.
Reeve 2008 {published data only}
-
- Reeve K, Rossiter K, Risdon C. The Last Straw! A board game on the social determinants of health. Medical Education 2008;42(11):1125‐6. - PubMed
Regan 2000 {published data only}
-
- Regan R. The effect of gaming on the empathic communication of associate degree nursing students [PhD thesis]. The effect of gaming on the empathic communication of associate degree nursing students [PhD thesis]. Chester, PA: Widener University School of Nursing, 2000.
Reiner 2008 {published data only}
-
- Reiner B. The potential for gmaing techniques in radiology education and practice. American College of Radiology 2008;5(2):110‐4. - PubMed
Roubidoux 2002 {published data only}
-
- Roubidoux MA, Chapman CM, Piontek ME. Development and evaluation of an interactive Web‐based breast imaging game for medical students. Academic Radiology 2002;9(10):1169‐78. - PubMed
Saethang 1998 {published data only}
-
- Saethang T, Kee CC. A gaming strategy for teaching the use of critical cardiovascular drugs. Erratum in: J Contin Educ Nurs 1998 May‐Jun;29(3):144.. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 1998;29(2):61‐5. [PUBMED: 9582773] - PubMed
Schmitz 1991 {published data only}
-
- Schmitz BD, MacLean SL, Shidler HM. An emergency pursuit game: a method for teaching emergency decision‐making skills. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 1991;22(4):152‐8. - PubMed
Silva 1989 {published data only}
-
- Silva JR, Deck ML. The games we play. Journal of Pediatric Nursing 1989;4(1):59‐61. - PubMed
Sisson 1988 {published data only}
-
- Sisson PM, Becker LM. Using games in nursing education. Journal for Nurses in Staff Development 1988;4(4):146‐51. - PubMed
Skinner 2000 {published data only}
-
- Skinner KD. Creating a game for sexuality and aging: the Sexual Dysfunction Trivia game. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 2000;31(4):185‐9. - PubMed
Stefanelli 1992 {published data only}
-
- Stefanelli MC. Playing and learning nurse‐patient communication [Jogando e aprendendo comunicacao enfermeira‐paciente]. Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP 1992;26(2):219‐34. [PUBMED: 129502] - PubMed
Stephenson 1998 {published data only}
-
- Stephenson NL, Lee BT. Creative strategies for updating knowledge on sexually transmitted diseases. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 1998;29(1):32‐4. - PubMed
Stewart 2006 {published data only}
-
- Stewart S. Skin care jeopardy: an innovative way of providing education for care partners on pressure ulcer prevention. Journal of wound, ostomy, and continence nursing 2006;33(3S):S34.
Sturgis 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sturgis G, McNatt P, Jones S. Batter up ‐‐ hitting a home run with ECCO implementation. Critical Care Nurse 2006;26(2):S29.
Taekman 2010 {published data only}
-
- Taekman JM, Shelley K. Virtual environments in healthcare: immersion, disruption, and flow. International Anesthesiology Clinics 2010;48(3):101‐21. - PubMed
Thornburg 1998 {published data only}
-
- Thornburg N. Teaching strategies. No time for education? Creative teaching tools for educators. Home Healthcare Nurse Manager 1998;2(6):7‐8;13. [PUBMED: 10646347] - PubMed
Tumosa 2006 {published data only}
-
- Tumosa N, Morley JE. The use of games to improve patient outcomes. Gerontology & Geriatrics Education 2006;26(4):37‐45. - PubMed
Turley 2007 {published data only}
-
- Turley CB, Roach R, Marx M. Systems survivor: a program for house staff in systems‐based practice. Teaching and Learning in Medicine 2007;19(2):128‐38. - PubMed
Udin 1985 {published data only}
-
- Udin RD, Kuster CG. A board game for sensitizing dental students to children with special needs. Journal of Dental Education 1985;49(2):111‐4. - PubMed
Verdaasdonk 2009 {published data only}
-
- Verdaasdonk EG, Dankelman J, Schijven MP, Lange JF, Wentink M, Stassen LP. Serious gaming and voluntary laparoscopic skills training: a multicenter study. Minimally Invasive Therapy & Allied Technologies 2009;18(4):232‐38. - PubMed
Wargo 2000 {published data only}
-
- Wargo CA. Blood Clot: gaming to reinforce learning about disseminated intravascular coagulation. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 2000;31(4):149‐51. - PubMed
Warihay 1986 {published data only}
-
- Warihay PD, Kanouse DN. Nursing management: playing to win. The American Journal of Nursing 1986;86(3):276‐7. - PubMed
White 1985 {published data only}
-
- White MJ. Cost‐containment: playing the money game. Nursing Success Today 1985;2(3):11‐3. - PubMed
Wilson 1995 {published data only}
-
- Wilson SM. The development and evaluation of a gaming strategy to teach metered dose inhaler use to home care nurses [Master's thesis]. Pittsburgh, PA: Duquesne University School of Nursing, 1995.
Additional references
Akl 2010a
-
- Akl EA, Pretorius RW, Sackett K, Erdley WS, Bhoopathi PS, Alfarah Z, et al. The effect of educational games on medical students' learning outcomes: a systematic review. BEME Guide No. 14. Medical Teacher 2010;1:16‐27. - PubMed
Allery 2004
-
- Allery LA. Educational games and structured experiences. Medical Teacher 2004;26(6):504‐5. - PubMed
Beach 2004
-
- Beach MC, Cooper LA, Robinson KA, Price EG, Gary TL, Jenckes MW, et al. Strategies for improving minority healthcare quality. Summary. Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 90. AHRQ Pub. No. 04‐E008‐1. AHRQ Pub. No. 04‐E008‐1. http://archive.ahrq.gov/clinic/epcsums/minqusum.pdf. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, 2004. - PMC - PubMed
Berdemeier 1982
-
- Berdemeier ME, Bernstein G, Oxman W. Bafa Bafa and dogmatism/ethnocentrism. Simulation & Games 1982;13:413‐36.
Blenner 1991
-
- Blenner JL. Researcher for a day: a simulation game. Nurse Educator 1991;16(2):32‐5. - PubMed
Bonwell 1991
-
- Bonwell CC, Eison JA. Active Learning: Creating Excitement in the Classroom. Washington, DC: George Washington University, 1991.
Boocock 1968
-
- Boocock SS, Schild EO. Simulation Games in Learning. Beverly Hills, CA: Sage Publications, 1968.
Byrum 1996
-
- Byrum CD, Rudisill PT, Singletary MB. The Traveling Salvation Show. A performance‐centered skills fair. Journal of Nursing Staff Development 1996;12(4):198‐203. - PubMed
Calliari 1991
-
- Calliari D. Using games to make learning fun. Rehabilitation Nursing 1991;16(3):154‐5. - PubMed
Carroll 1991
-
- Carroll P. Using multiple teaching techniques in a continuing education program. Focus on Critical Care 1991;18(6):502‐5. - PubMed
Clark 1976
-
- Clark CC. Simulation gaming: a new teaching strategy in nursing education. Nurse Educator 1976;1(4):4‐9. - PubMed
Corbett 1982
-
- Corbett NA, Beveridge P. Simulation as a tool for learning. Topics in Clinical Nursing 1982;4(3):58‐67. - PubMed
Crancer 1980
-
- Crancer J, Maury‐Hess S. Games: an alternative to pedagogical instruction. Journal of Nursing Education 1980;19(3):45‐52. - PubMed
Draper 1981
-
- Draper N, Smith H. Applied Regression Analysis. New York: Wiley, 1981.
Fitzgerald 1997
-
- Fitzgerald K. Instructional methods: selection, use, and evaluation. In: Bastable SB editor(s). Nurse as Educator: Principles of Teaching and Learning. Sudbury, MA: Jones and Bartlett, 1997:261‐86.
Gordon 1970
-
- Gordon AK. Games for Growth; Educational Games in the Classroom. Palo Alto, CA: Science Research Associates, 1970.
Haak 1990
-
- Haak SW, Burton S, Birka AM, Carlin MA, Davey SS, Hujcs M, et al. Clinical judgment: an instructional game for nursing. Nurse Educator 1990;15(4):11, 20, 28. - PubMed
Hankinson 1987
-
- Hankinson H, Jr. The Coginitive and Affective Learning Effects of Debriefing After a Simulation Game [PhD thesis]. [Bloomington], IN: Indiana University.
Hayes 2000
-
- Hayes SK, Childress DM. Games galore. Journal for Nurses in Staff Development 2000;16(4):168‐70. - PubMed
Hays 1989
-
- Hays JC. Beyond the windshield: scavenging community data. Nurse Educator 1989;14(3):12‐6. - PubMed
Horizon Report 2006
-
- New Media Consortium, EDUCAUSE. http//www.nmc.org/pdf/2006_Horizon_Report.pdf. Austin, TX: New Media Consortium, 2006.
Howell 2005
-
- Howell K. Games for health conference 2004: issues, trends, and needs unique to games for health. Cyberpsychology & Behavior 2005;8(2):103‐9. - PubMed
Joyce 1986
-
- Joyce BR, Weil M. Models of teaching. 3rd Edition. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice‐Hall, 1986.
Kenny 2003
-
- Kenny LJ. Using Edward de Bono's six hats game to aid critical thinking and reflection in palliative care. International Journal of Palliative Nursing 2003;9(3):105‐12. - PubMed
Knowles 1970
-
- Knowles MS. The modern practice of adult education; andragogy versus pedagogy. New York, NY: Association Press, 1970.
Kolb 1984
-
- Kolb DA. Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice‐Hall, 1984.
Laird 1990
-
- Laird N, Mosteller F. Some statistical methods for combining experimental results. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care 1990;6:5‐30. - PubMed
Lewis 1989
-
- Lewis DJ, Saydak SJ, Mierzwa IP, Robinson JA. Gaming: a teaching strategy for adult learners. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 1989;20(2):80‐4. - PubMed
McDougal 1992
-
- McDougal JE. Bringing electrolytes to life: an imagery game. Nurse Educator 1992;17(6):8‐10. - PubMed
Ormiston 2001
-
- Ormiston M. Jeopardy Templates and Other Games. techteachers.com/jeopardytemplates.htm (accessed Dec 2012) 2001.
Pfeiffer 1980
-
- Pfeiffer JW, Jones JE. Structured Experience Kit: Users Guide. San Diego: University Associates, 1980.
Reed 2005
-
- Reed D, Price EG, Windish DM, Wright SM, Gozu A, Hsu EB, et al. Challenges in systematic reviews of educational intervention studies. Annals of Internal Medicine 2005;142(12 Pt 2):1080‐9. - PubMed
Rowles 1998
-
- Rowles CJ, Brigham C. Strategies to promote critical thinking and active learning. In: Billings DM, Halstead, JA editor(s). Teaching in Nursing: A Guide for Faculty. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, 1998:247‐74.
Shubik 1989
-
- Shubik M. Gaming: theory and practice, past and future. Simulation & Games 1989;20(2):184‐89.
Speers 1993
-
- Speers AT. Games in nursing staff development. Journal of Nursing Staff Development 1993;9(6):274‐7. - PubMed
Sprengel 1992
-
- Sprengel AD. A Study of the Attainment of Diabetes Concepts using a Simulation‐Gaming Instructional Strategy [PhD thesis]. [Memphis]: Memphis State University, 1992.
Stern 1989
-
- Stern SB, Cooper SS. Creative teaching strategies. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 1989;20(2):95‐6. - PubMed
Taylor 1972
-
- Taylor JL, Walford R. Simulation in the classroom: an introduction to role‐play, games and simulation in education. Harmondsworth: Penguin, 1972.
Thatcher 1990
-
- Thatcher DC. Promoting learning through games and simulations. Simulation and Gaming 1990;21(3):262‐73.
Ukoumunne 1999
-
- Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ. Methods for evaluating area‐wide and organisation based interventions in health and health care: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment 1999;3(5):1‐108. - PubMed
Waddell 1994
-
- Waddell DL, Summers AD, Hummel ME. Creative strategies for teaching nursing research. Nurse Educator 1994;19(5):5‐6. - PubMed
Walljasper 1982
-
- Walljasper D. Games with goals. Nurse Educator 1982;7(1):15‐8. - PubMed
Wolfe 1993
-
- Wolfe J. A history of business teaching games in English speaking and post socialist countries: the origination and diffusion of a management education and development technology. Simulation & Gaming 1993;24(4):446‐63.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources