Anti-TNF-α treatment for pelvic pain associated with endometriosis
- PMID: 23543560
- PMCID: PMC11366413
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008088.pub3
Anti-TNF-α treatment for pelvic pain associated with endometriosis
Abstract
Background: Endometriosis is a chronic, recurring condition that can develop during the reproductive years. It is characterised by the development of endometrial tissue outside the uterine cavity. It is the most common cause of pelvic pain in women. This endometrial tissue development is dependent on oestrogen produced primarily by the ovaries and, therefore, traditional management has focused on suppression of ovarian function. Mounting evidence shows that altered immune function plays a crucial role in the genesis and development of endometriosis. In this review we considered modulation of the inflammation as an alternative approach.
Objectives: To determine the effectiveness and safety of anti-tumour necrosis factor-α (anti-TNF-α) treatment in the management of endometriosis in premenopausal women.
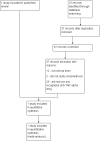
Search methods: For the first publication of this review, we searched for trials in the following databases (from their inception to August 2009): Cochrane Menstrual Disorders and Subfertility Group Specialised Register, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library), MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, and PsycINFO. In addition, we searched all reference lists of included trials and contacted experts in the field in an attempt to locate trials. We reran this search to 3 September 2012 for this update.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing anti-TNF-α drugs with placebo, no treatment, medical treatment, or surgery for pelvic pain associated with endometriosis were included.
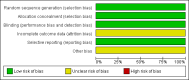
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently selected trials for inclusion, assessed trial quality, and extracted data using data extraction forms. The domains assessed for risk of bias were sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding, incomplete outcome data, and selective outcome reporting. We used risk ratios (RR) for reporting dichotomous data with 95% confidence intervals (CI), whilst we expressed continuous data as mean differences (MD). We assessed statistical heterogeneity using the I(2) statistic.
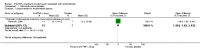
Main results: Only one trial involving 21 participants was included. The results showed no evidence of an effect of infliximab, one of the known anti-TNF-α drugs, on pelvic pain reduction using the Biberoglu-Behrman (BB) score (0 to 3 scale) for participants (MD -0.14, 95% CI -0.43 to 0.15), the BB score for clinicians (MD -0.14, 95% CI -0.39 to 0.11), or a visual analogue pain score (VAS, 100 mm scale) (MD -5.60, 95% CI -16.10 to 4.90), or on the use of pain killers (ibuprofen, g/day) (MD -0.10, 95% CI -0.30 to 0.10). There was no evidence of an increase in adverse events in the infliximab group compared with placebo (RR 3.73, 95% CI 0.22 to 63.66). We found no evidence of clinical benefits of infliximab for endometriotic lesions, dysmenorrhoea, dyspareunia, or pelvic tenderness. To date, there is no trial that has reported a cost-effectiveness analysis of anti-TNF-α drugs, or the odds of recurrence.
Authors' conclusions: This review was updated in 2012. The results of the original review published in 2010 remain unchanged. There is still not enough evidence to support the use of anti-TNF-α drugs in the management of women with endometriosis for the relief of pelvic pain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that all the analysis and interpretation reflected the opinions of the authors; no conflict of interest was involved in the analysis or interpretation of data, or in the writing of the systematic review.
Figures


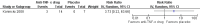





Update of
-
Anti-TNF-alpha treatment for pelvic pain associated with endometriosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Mar 17;(3):CD008088. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008088.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Mar 28;(3):CD008088. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008088.pub3. PMID: 20238362 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
Lian 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lian F, Li XL, Sun ZG, Zhang JW, Liu YH, Ma FM. Effect of Quyu Jiedu granule on microenvironment of ova in patients with endometriosis. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine 2009;15(1):42‐6. - PubMed
Additional references
Anaf 2006
-
- Anaf V, Chapron C, Nakadi I, Moor V, Simonart T, Noel JC. Pain, mast cells, and nerves in peritoneal, ovarian, and deep infiltrating endometriosis. Fertility and Sterility 2006;86:1336‐43. - PubMed
ASRM 1997
-
- American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Revised American Society for Reproductive Medicine classification of endometriosis: 1996. Fertility and Sterility 1997;67:817‐21. - PubMed
Balasch 1997
-
- Balasch J, Creus M, Fabregues F, Carmona F, Martinez‐Roman S, Manau D, et al. Pentoxifylline versus placebo in the treatment of infertility associated with minimal or mild endometriosis: a pilot randomized clinical trial. Human Reproduction 1997;12:2046‐50. - PubMed
Barrier 2004
-
- Barrier BF, Bates GW, Leland MM, Leach DA, Robinson RD, Propst MA. Efficacy of anti‐tumor necrosis factor therapy in the treatment of spontaneous endometriosis in baboons. Fertility and Sterility 2004;81 Suppl 1:775‐9. - PubMed
Berkkanoglu 2003
-
- Berkkanoglu M, Arici A. Immunology and endometriosis. American Journal of Reproductive Immunology 2003;50(1):48‐59. - PubMed
Braun 1998
-
- Braun DP, Dmowski WP. Endometriosis: abnormal endometrium and dysfunctional immune response. Current Opinion in Obstetrics and Gynecology 1998;10:365‐9. - PubMed
Braun 2002
-
- Braun DP, Ding J, Dmowski WP. Peritoneal fluid‐mediated enhancement of eutopic and ectopic endometrial cell proliferation is dependent on tumor necrosis factor‐alpha in women with endometriosis. Fertility and Sterility 2002;78:727‐32. - PubMed
Brosens 1997
-
- Brosens IA. Endometriosis ‐ a disease because it is characterized by bleeding. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1997;176:263‐7. - PubMed
Bullimore 2003
-
- Bullimore DW. Endometriosis is sustained by tumour necrosis factor‐alpha. Medical Hypotheses 2003;60(1):84‐8. - PubMed
Child 2001
-
- Child TJ, Tan SL. Endometriosis: aetiology, pathogenesis and treatment. Drugs 2001;61:1735‐50. - PubMed
Christodoulakos 2007
-
- Christodoulakos G, Augoulea A, Lambrinoudaki I, Sioulas V, Creatsas G. Pathogenesis of endometriosis: the role of defective 'immunosurveillance'. European Journal of Contraception and Reproductive Health Care 2007;12:194‐202. - PubMed
D'Antonio 2000
-
- D'Antonio M, Martelli F, Peano S, Papoian R, Borrelli F. Ability of recombinant human TNF binding protein‐1 (r‐hTBP‐1) to inhibit the development of experimentally induced endometriosis in rats. Journal of Reproductive Immunology 2000;48:81‐98. - PubMed
D'Hooghe 2001
-
- D'Hooghe TM, Cuneo S, Nugent N, Chai D, Deer F, Mwenda J. Recombinant human TNF binding protein‐1 (r‐hTBP‐1) inhibits the development of endometriosis in baboons: a prospective, randomized, placebo and drug‐controlled study. Fertility and Sterility 2001;76 Suppl 1:1.
D'Hooghe 2002
-
- D'Hooghe TM, Debrock S. Endometriosis, retrograde menstruation and peritoneal inflammation in women and in baboons. Human Reproduction Update 2002;8(1):84‐8. - PubMed
D'Hooghe 2003
-
- D'Hooghe TM, Debrock S, Hill JA, Meuleman C. Endometriosis and subfertility: is the relationship resolved?. Seminars in Reproductive Medicine 2003;21:243‐54. - PubMed
Davis 2007
Egger 1997
Eisermann 1988
-
- Eisermann J, Gast MJ, Pineda J, Odem RR, Collins JL. Tumor necrosis factor in peritoneal fluid of women undergoing laparoscopic surgery. Fertility and Sterility 1988;50:573‐9. - PubMed
Falconer 2004
-
- Falconer H, Mwenda JM, Chai DC, Wagner C, Cornillie FJ, D'Hooghe TM. Treatment with anti‐TNF antibody c5N reduces the extent of induced endometriosis in the baboon. Fertility and Sterility 2004;82 Suppl 2:54‐5. - PubMed
Falconer 2008
-
- Falconer H, Mwenda JM, Chai DC, Song XR, Cornillie FJ, Bergqvist A, et al. Effects of anti‐TNF‐mAb treatment on pregnancy in baboons with induced endometriosis. Fertility and Sterility 2008;89(5):1537‐45. - PubMed
Halme 1984
-
- Halme J, Becker S, Wing R. Accentuated cyclic activation of peritoneal macrophages in patients with endometriosis. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1984;148:85‐90. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Ingelmo 1999
-
- Ingelmo JM, Quereda F, Acien P. Intraperitoneal and subcutaneous treatment of experimental endometriosis with recombinant human interferon‐alpha‐2b in murine model. Fertility and Sterility 1999;71:907‐11. - PubMed
Iwabe 2000
-
- Iwabe T, Harada T, Tsudo T, Nagano Y, Yoshida S, Tanikawa M, et al. Tumor necrosis factor‐alpha promote proliferation of endometriotic stromal cells by inducing interleukin‐8 gene and protein expression. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2000;85:824‐9. - PubMed
Keenan 1995
-
- Keenan JA, Chen TT, Chadwell NL, Torry DS, Caudle MR. IL‐1 beta, TNF‐alpha, and IL‐2 in peritoneal fluid and macrophage‐conditioned media of women with endometriosis. American Journal of Reproductive Immunology 1995;34:381‐5. - PubMed
Keenan 2000
-
- Keenan JA, Williams‐Boyce PK, Massey PJ, Chen TT, Caudle MR, Bukovsky A. Regression of endometrial explants in a rat model of endometriosis treated with immune modulators loxoribine and levamisole. Fertility and Sterility 2000;72:135‐41. - PubMed
Kennedy 2005
-
- Kennedy S, Bergqvist A, Chapron C, D'Hooghe T, Duselman G, Greb R, et al. ESHRE guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis. Human Reproduction 2005;20(10):2698‐704. - PubMed
Kyama 2008
-
- Kyama CM, Overbergh L, Mihalyi A, Cuneo S, Chai D, Debrock S, et al. Effect of recombinant human TNF‐binding protein‐1 and GnRH antagonist on mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines and adhesion and growth factors in endometrium and endometriosis tissues in baboons. Fertility and Sterility 2008;89 Suppl 5:1306‐13. - PubMed
Lebovic 2001
-
- Lebovic DI, Mueller MD, Taylor RN. Immunobiology of endometriosis. Fertility and Sterility 2001;75(1):1‐10. - PubMed
Lee 2008
-
- Lee GH, Choi YM, Kim SH, Hong MA, Oh ST, Lim YT, et al. Association of tumor necrosis factor‐a gene polymorphisms with advanced stage endometriosis. Human Reproduction 2008;23(4):977‐81. - PubMed
Ling 1999
-
- Ling FW. Randomized controlled trial of depot leuprolide in patients with chronic pelvic pain and clinically suspected endometriosis. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1999;37:51‐8. - PubMed
Olive 2003
-
- Olive DL, Pritts EA. Treatment of endometriosis. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;345(4):266‐75. - PubMed
Oosterlynck 1991
-
- Oosterlynck DJ, Cornillie FJ, Waer M, Vandeputte M, Koninckx PR. Women with endometriosis show a defect in natural killer activity resulting in a decreased cytotoxicity to autologous endometrium. Fertility and Sterility 1991;56:45‐51. - PubMed
Oosterlynck 1993
-
- Oosterlynck DJ, Meuleman C, Sobis H, Vandeputte M, Koninckx PR. Angiogenic activity of peritoneal fluid from women with endometriosis. Fertility and Sterility 1993;59:778‐82. - PubMed
Possover 2007
-
- Possover M, Chiantera V. Isolated infiltrative endometriosis of the sciatic nerve: a report of three patients. Fertility and Sterility 2007;87:417‐9. - PubMed
Prentice 1999
-
- Prentice A, Deary A, Goldbeck‐Wood S, Farquhar CM, Smith S. Gonadotrophin‐releasing hormone analogues for pain associated with endometriosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1999, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000346.pub2] - DOI
Prentice 2000
RCOG 2006
-
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG). The investigation and management of endometriosis. London (UK): Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) 2006.
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Ridder 2007
-
- Ridder LD, Benninga MA, Tamminiau JA, Hommes DW, Deventer SJ. Infliximab use in children and adolescents with inflammatory bowel disease. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2007;45:3‐14. - PubMed
Robert 1998
-
- Robert R, Prat‐Pradal D, Labat JJ, Bensignor M, Raoul S, Rebai R, et al. Anatomic basis of chronic perineal pain: role of the pudendal nerve. Radiologic Anatomy 1998;20:93‐8. - PubMed
Selak 2007
Siristatidis 2006
-
- Siristatidis C, Nissotakis C, Chrelias C, Iacovidou H, Salamalekis E. Immunological factors and their role in the genesis and development of endometriosis. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research 2006;32(2):162‐70. - PubMed
Somigliana 1999
-
- Somigliana E, Vigano P, Rossi G, Carinelli S, Vignali M, Panina‐Bordignon P. Endometrial ability to implant in ectopic sites can be prevented by interleukin‐12 ina murine model of endometriosis. Human Reproduction 1999;14:2944‐50. - PubMed
Taylor 1997
-
- Taylor RN, Ryan IP, Moore ES, Hornung D, Shifren JL, Tseng JF. Angiogenesis and macrophage activation in endometriosis. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1997;828:194‐207. - PubMed
Teramoto 2004
-
- Teramoto M, Kitawaki J, Koshiba H, Kitaoka Y, Obayashi H, Hasegawa G, et al. Genetic contribution of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)‐alpha gene promoter (‐1031,‐863 and ‐857) and TNF receptor 2 gene polymorphisms in endometriosis susceptibility. American Journal of Reproductive Immunology 2004;51:352‐7. - PubMed
Viganò 2003
-
- Viganò P, Mangioni S, Odorizzi MP, Chiodini A, Rocca S, Chiodo I. Use of estrogen antagonists and aromatase inhibitors in endometriosis. Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs 2003;4:1209‐12. - PubMed
Winkel 2000
-
- Winkel CA. A cost‐effective approach to the management of endometriosis. Current Opinion in Obstetrics and Gynecology 2000;12:317‐20. - PubMed
Winkel 2003
-
- Winkel CA. Evaluation and management of women with endometriosis. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2003;102:397‐408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

