Genomic dissection of Hurthle cell carcinoma reveals a unique class of thyroid malignancy
- PMID: 23543667
- PMCID: PMC5393465
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2012-3539
Genomic dissection of Hurthle cell carcinoma reveals a unique class of thyroid malignancy
Abstract
Context: Hurthle cell cancer (HCC) is an understudied cancer with poor prognosis.
Objective: Our objective was to elucidate the genomic foundations of HCC.
Design and setting: We conducted a large-scale integrated analysis of mutations, gene expression profiles, and copy number alterations in HCC at a single tertiary-care cancer institution.
Methods: Mass spectrometry-based genotyping was used to interrogate hot spot point mutations in the most common thyroid oncogenes: BRAF, RET, NRAS, HRAS, KRAS, PIK3CA, MAP2K1, and AKT1. In addition, common oncogenic fusions of RET and NTRK1 as well as PAX8/PPARγ and AKAP9-BRAF were also assessed by RT-PCR. Global copy number changes and gene expression profiles were determined in the same tumor set as the mutational analyses.
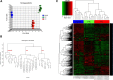
Results: We report that the mutational, transcriptional, and copy number profiles of HCC were distinct from those of papillary thyroid cancer and follicular thyroid cancer, indicating HCC to be a unique type of thyroid malignancy. Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of gene expression showed the 3 groups of Hurthle tumors (Hurthle cell adenoma [HA], minimally invasive Hurthle cell carcinoma [HMIN], and widely invasive Hurthle cell carcinoma [HWIDE] clustered separately with a marked difference between HWIDE and HA. Global copy number analysis also indicated distinct subgroups of tumors that may arise as HWIDE and HMIN. Molecular pathways that differentiate HA from HWIDE included the PIK3CA-Akt-mTOR and Wnt/β-catenin pathways, potentially providing a rationale for new targets for this type of malignancy.
Conclusions: Our data provide evidence that HCC may be a unique thyroid cancer distinct from papillary and follicular thyroid cancer.
Figures





References
-
- Hundahl SA , Fleming ID , Fremgen AM , Menck HR. A National Cancer Data Base report on 58,856 cases of thyroid carcinoma treated in U.S., 1985–1995. Cancer. 1998;83:2638–2648. - PubMed
-
- Montone KT , Baloch ZW , LiVolsi VA. The thyroid Hürthle (oncocytic) cell and its associated pathologic conditions: a surgical pathology and cytopathology review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008;132:1241–1250. - PubMed
-
- Ghossein RA , Hiltzik DH , Carlson DL , et al. . Prognostic factors of recurrence in encapsulated Hurthle cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland: a clinicopathologic study of 50 cases. Cancer. 2006;106(8):1669–1676. - PubMed
-
- Shaha AR , Shah JP , Loree TR. Patterns of nodal and distant metastasis based on histologic varieties in differentiated carcinoma of the thyroid. Am J Surg. 1996;172:692–694. - PubMed
-
- Grossman RF , Clark OH. Hurthle cell carcinoma. Cancer Control. 1997;4:13–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

