Cutting Edge: memory regulatory t cells require IL-7 and not IL-2 for their maintenance in peripheral tissues
- PMID: 23543753
- PMCID: PMC3660612
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300212
Cutting Edge: memory regulatory t cells require IL-7 and not IL-2 for their maintenance in peripheral tissues
Abstract
Thymic Foxp3-expressing regulatory T cells are activated by peripheral self-antigen to increase their suppressive function, and a fraction of these cells survive as memory regulatory T cells (mTregs). mTregs persist in nonlymphoid tissue after cessation of Ag expression and have enhanced capacity to suppress tissue-specific autoimmunity. In this study, we show that murine mTregs express specific effector memory T cell markers and localize preferentially to hair follicles in skin. Memory Tregs express high levels of both IL-2Rα and IL-7Rα. Using a genetic-deletion approach, we show that IL-2 is required to generate mTregs from naive CD4(+) T cell precursors in vivo. However, IL-2 is not required to maintain these cells in the skin and skin-draining lymph nodes. Conversely, IL-7 is essential for maintaining mTregs in skin in the steady state. These results elucidate the fundamental biology of mTregs and show that IL-7 plays an important role in their survival in skin.
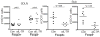
Figures



References
-
- Bennett CL, Christie J, Ramsdell F, Brunkow ME, Ferguson PJ, Whitesell L, Kelly TE, Saulsbury FT, Chance PF, Ochs HD. The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat Genet. 2001;27:20–21. - PubMed
-
- Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:330–336. - PubMed
-
- Miyara M, Yoshioka Y, Kitoh A, Shima T, Wing K, Niwa A, Parizot C, Taflin C, Heike T, Valeyre D, Mathian A, Nakahata T, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M, Amoura Z, Gorochov G, Sakaguchi S. Functional delineation and differentiation dynamics of human CD4+ T cells expressing the FoxP3 transcription factor. Immunity. 2009;30:899–911. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

