Genome-wide association study in BRCA1 mutation carriers identifies novel loci associated with breast and ovarian cancer risk
- PMID: 23544013
- PMCID: PMC3609646
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003212
Genome-wide association study in BRCA1 mutation carriers identifies novel loci associated with breast and ovarian cancer risk
Abstract
BRCA1-associated breast and ovarian cancer risks can be modified by common genetic variants. To identify further cancer risk-modifying loci, we performed a multi-stage GWAS of 11,705 BRCA1 carriers (of whom 5,920 were diagnosed with breast and 1,839 were diagnosed with ovarian cancer), with a further replication in an additional sample of 2,646 BRCA1 carriers. We identified a novel breast cancer risk modifier locus at 1q32 for BRCA1 carriers (rs2290854, P = 2.7 × 10(-8), HR = 1.14, 95% CI: 1.09-1.20). In addition, we identified two novel ovarian cancer risk modifier loci: 17q21.31 (rs17631303, P = 1.4 × 10(-8), HR = 1.27, 95% CI: 1.17-1.38) and 4q32.3 (rs4691139, P = 3.4 × 10(-8), HR = 1.20, 95% CI: 1.17-1.38). The 4q32.3 locus was not associated with ovarian cancer risk in the general population or BRCA2 carriers, suggesting a BRCA1-specific association. The 17q21.31 locus was also associated with ovarian cancer risk in 8,211 BRCA2 carriers (P = 2×10(-4)). These loci may lead to an improved understanding of the etiology of breast and ovarian tumors in BRCA1 carriers. Based on the joint distribution of the known BRCA1 breast cancer risk-modifying loci, we estimated that the breast cancer lifetime risks for the 5% of BRCA1 carriers at lowest risk are 28%-50% compared to 81%-100% for the 5% at highest risk. Similarly, based on the known ovarian cancer risk-modifying loci, the 5% of BRCA1 carriers at lowest risk have an estimated lifetime risk of developing ovarian cancer of 28% or lower, whereas the 5% at highest risk will have a risk of 63% or higher. Such differences in risk may have important implications for risk prediction and clinical management for BRCA1 carriers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

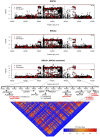
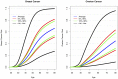
References
-
- Antoniou AC, Chenevix-Trench G (2010) Common genetic variants and cancer risk in Mendelian cancer syndromes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 20: 299–307 S0959-437X(10)00044-4 [pii];10.1016/j.gde.2010.03.010 [doi]. - PubMed
-
- Couch FJ, Gaudet MM, Antoniou AC, Ramus SJ, Kuchenbaecker KB, et al. (2012) Common cariants at the 19p13.1 and ZNF365 loci are associated with ER subtypes of breast cancer and ovarian cancer risk in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 21: 645–657 1055-9965.EPI-11-0888 [pii];10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-11-0888 [doi]. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR025764/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 11174/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA083855/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA102776/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-06-503/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA069446/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES009089/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA069417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA16094/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA069638/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA116201/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140323/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA140323/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA128978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 CA092049/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA102776/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC4 CA153828/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA101165/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA69417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C5047/A8385/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA069467/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA22435/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16565/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 11022/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- N02-CP-11019-50/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C12292/A11174/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- CA 27469/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA069398/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA027469/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA128978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N02 CP011019/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N02 CP065504/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA116201/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA74415/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 101165/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA113916/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA069631/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037517/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA69398/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC4A153828/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- 15007/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01-CA083855/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA033752/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013696/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01CA113916/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA69638/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA149429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA69446/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 37517/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA69631/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA022435/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N02-CP-65504/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C1287/A11990/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA074415/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 10118/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C1287/A10118/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA69467/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA13696/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA042014/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

