Evidence of gene-environment interactions between common breast cancer susceptibility loci and established environmental risk factors
- PMID: 23544014
- PMCID: PMC3609648
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003284
Evidence of gene-environment interactions between common breast cancer susceptibility loci and established environmental risk factors
Abstract
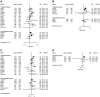
Various common genetic susceptibility loci have been identified for breast cancer; however, it is unclear how they combine with lifestyle/environmental risk factors to influence risk. We undertook an international collaborative study to assess gene-environment interaction for risk of breast cancer. Data from 24 studies of the Breast Cancer Association Consortium were pooled. Using up to 34,793 invasive breast cancers and 41,099 controls, we examined whether the relative risks associated with 23 single nucleotide polymorphisms were modified by 10 established environmental risk factors (age at menarche, parity, breastfeeding, body mass index, height, oral contraceptive use, menopausal hormone therapy use, alcohol consumption, cigarette smoking, physical activity) in women of European ancestry. We used logistic regression models stratified by study and adjusted for age and performed likelihood ratio tests to assess gene-environment interactions. All statistical tests were two-sided. We replicated previously reported potential interactions between LSP1-rs3817198 and parity (Pinteraction = 2.4 × 10(-6)) and between CASP8-rs17468277 and alcohol consumption (Pinteraction = 3.1 × 10(-4)). Overall, the per-allele odds ratio (95% confidence interval) for LSP1-rs3817198 was 1.08 (1.01-1.16) in nulliparous women and ranged from 1.03 (0.96-1.10) in parous women with one birth to 1.26 (1.16-1.37) in women with at least four births. For CASP8-rs17468277, the per-allele OR was 0.91 (0.85-0.98) in those with an alcohol intake of <20 g/day and 1.45 (1.14-1.85) in those who drank ≥ 20 g/day. Additionally, interaction was found between 1p11.2-rs11249433 and ever being parous (Pinteraction = 5.3 × 10(-5)), with a per-allele OR of 1.14 (1.11-1.17) in parous women and 0.98 (0.92-1.05) in nulliparous women. These data provide first strong evidence that the risk of breast cancer associated with some common genetic variants may vary with environmental risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Kawase T, Matsuo K, Suzuki T, Hiraki A, Watanabe M, et al. (2009) FGFR2 intronic polymorphisms interact with reproductive risk factors of breast cancer: results of a case control study in Japan. Int J Cancer 125: 1946–1952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 CA069417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA128978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA69417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C490/A10119/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA069467/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16565/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA069398/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C490/A10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA128978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200900010C/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA047147/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA116201/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA69664/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA77398/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-06-503/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA069446/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 10118/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA047305/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA069638/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA116201/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 CA092049/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C490/A6187/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 11022/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- CA122340/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C1287/A12014/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA069631/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA077398/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA69638/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- K05 CA152715/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA69398/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA69446/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA69631/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA069664/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122340/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C1287/A10118/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA47147/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16561/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 2004NOV49/BBC_/Breast Cancer Now/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

