IL-10 dependent suppression of type 1, type 2 and type 17 cytokines in active pulmonary tuberculosis
- PMID: 23544075
- PMCID: PMC3609860
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059572
IL-10 dependent suppression of type 1, type 2 and type 17 cytokines in active pulmonary tuberculosis
Abstract
Background: Although Type 1 cytokine responses are considered protective in pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB), their role as well as those of Type 2, 17 and immunoregulatory cytokines in tuberculous lymphadenitis (TBL) and latent tuberculosis (LTB) have not been well studied.
Aim and methods: To identify cytokine responses associated with pulmonary tuberculosis (TB), TB lymphadenitits and latent TB, we examined mycobacterial antigen-specific immune responses of PTB, TBL and LTB individuals. More specifically, we examined ESAT-6 and CFP-10 induced Type 1, Type 2 and Type 17 cytokine production and their regulation using multiplex ELISA.
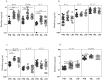
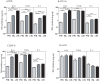
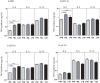
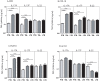
Results: PTB individuals exhibited a significantly lower baseline as well as antigen-specific production of Type 1 (IFNγ, TNFα and IL-2); Type 2 (IL-4) and Type 17 (IL-17A and IL-17F) cytokines in comparison to both TBL and LTB individuals. TBL individuals exhibited significantly lower antigen-specific IFNγ responses alone in comparison to LTB individuals. Although, IL-10 levels were not significantly higher, neutralization of IL-10 during antigen stimulation resulted in significantly enhanced production of IFNγ, IL-4 and IL-17A in PTB individuals, indicating that IL-10 mediates (at least partially) the suppression of cytokine responses in PTB.
Conclusion: Pulmonary TB is characterized by an IL-10 dependent antigen-specific suppression of Type 1, Type 2 and Type 17 cytokines, reflecting an important association of these cytokines in the pathogenesis of active TB.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Altered CD8(+) T cell frequency and function in tuberculous lymphadenitis.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2014 Sep;94(5):482-93. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2014.06.007. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2014. PMID: 25027793 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced systemic and mycobacterial antigen-stimulated concentrations of IL-1β and IL-18 in tuberculous lymphadenitis.Cytokine. 2017 Feb;90:66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2016.10.013. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Cytokine. 2017. PMID: 27794266 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Diminished type 1 and type 17 cytokine expressing - Natural killer cell frequencies in tuberculous lymphadenitis.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2019 Sep;118:101856. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2019.101856. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2019. PMID: 31430696
-
Modulation of Th1/Tc1 and Th17/Tc17 responses in pulmonary tuberculosis by IL-20 subfamily of cytokines.Cytokine. 2018 Aug;108:190-196. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.04.005. Epub 2018 Apr 21. Cytokine. 2018. PMID: 29684756 Free PMC article.
-
Helminth mediated modulation of the systemic and mycobacterial antigen - stimulated cytokine profiles in extra-pulmonary tuberculosis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Mar 21;13(3):e0007265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007265. eCollection 2019 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 30897083 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Modulation of lncRNA NEAT1 overturns the macrophages based immune response in M. tuberculosis infected patients via miR-373 regulation.J Appl Genet. 2024 May;65(2):321-329. doi: 10.1007/s13353-023-00808-1. Epub 2023 Nov 23. J Appl Genet. 2024. PMID: 37993738
-
IL-27 and TGFβ mediated expansion of Th1 and adaptive regulatory T cells expressing IL-10 correlates with bacterial burden and disease severity in pulmonary tuberculosis.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2015 Sep;3(3):289-99. doi: 10.1002/iid3.68. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2015. PMID: 26417443 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of isoniazid preventive therapy on immune responses to mycobacterium tuberculosis: an open label randomised, controlled, exploratory study.BMC Infect Dis. 2015 Oct 22;15:438. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1201-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26493989 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Shifted T Helper Cell Polarization in a Murine Staphylococcus aureus Mastitis Model.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 31;10(7):e0134797. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134797. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26230498 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Plasma Matrix Metalloproteinase and Tissue Inhibitors of Matrix Metalloproteinase Levels With Adverse Treatment Outcomes Among Patients With Pulmonary Tuberculosis.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Dec 1;3(12):e2027754. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.27754. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 33258908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walzl G, Ronacher K, Hanekom W, Scriba TJ, Zumla A (2011) Immunological biomarkers of tuberculosis. Nat Rev Immunol 11: 343–354. - PubMed
-
- Handa U, Mundi I, Mohan S (2012) Nodal tuberculosis revisited: a review. J Infect Dev Ctries 6: 6–12. - PubMed
-
- Holland SM (2007) Interferon gamma, IL-12, IL-12R and STAT-1 immunodeficiency diseases: disorders of the interface of innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol Res 38: 342–346. - PubMed
-
- Keane J, Gershon S, Wise RP, Mirabile-Levens E, Kasznica J, et al. (2001) Tuberculosis associated with infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor alpha-neutralizing agent. N Engl J Med 345: 1098–1104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

