Down-regulation of miR-21 Induces Differentiation of Chemoresistant Colon Cancer Cells and Enhances Susceptibility to Therapeutic Regimens
- PMID: 23544170
- PMCID: PMC3610548
- DOI: 10.1593/tlo.12397
Down-regulation of miR-21 Induces Differentiation of Chemoresistant Colon Cancer Cells and Enhances Susceptibility to Therapeutic Regimens
Abstract
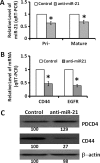
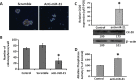
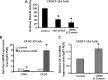
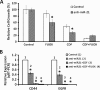
MicroRNAs are endogenous posttranscriptional modulators that negatively control the expression of their target genes and play an important role in the development and progression of many malignancies, including colorectal carcinoma. In particular, expression of microRNA-21 (miR-21) is greatly increased in chemotherapy-resistant (CR) colon cancer cells that are enriched in undifferentiated cancer stem/stem-like cells (CSCs/CSLCs). We hypothesize that miR-21 plays a critical role in regulating differentiation of CR colon cancer cells. Indeed, we observed that downregulation of miR-21 in CR colon cancer cells (HCT-116 or HT-29) by antisense miR-21 induced differentiation, as evidenced by marked increases in cytokeratin-20 (CK-20) expression and alkaline phosphatase activity. These changes were accompanied by a significant reduction in the expression of colon CSC/CSLC marker CD44, colonosphere formation, and T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor (TCF/LEF) activity but increased the expression of proapoptotic programmed cell death 4 gene. Induction of differentiation greatly increased sensitivity of CR colon cancer cells to the growth inhibitory properties of all three regimens tested: 5-fluorouracil + oxaliplatin (FUOX), difluorinated curcumin (CDF), and the combination of CDF and FUOX. However, the magnitude of inhibition of growth by either CDF (75%) alone or CDF + FUOX (80%) was much higher than that observed with only FUOX (40%). Growth inhibition by CDF and CDF + FUOX in differentiating CR colon cancer cells was associated with a 98% to 99% reduction in the expression of CD44 and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). However, down-regulation of CK-20 in CR colon cancer cells produced no significant change in cellular growth in the absence or presence of FUOX, when compared with the corresponding controls. The current observation suggests that CDF and CDF + FUOX are highly effective in inhibiting growth and reducing colon CSCs/CSLCs in anti-miR-21-induced differentiating CR colon cancer cells and supports our contention that differentiation enhances susceptibility of CR cancer cells to conventional and nonconventional therapeutic regimen.
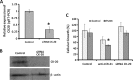
Figures
Similar articles
-
Omega-3 fatty acid is a potential preventive agent for recurrent colon cancer.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2014 Nov;7(11):1138-48. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-14-0177. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2014. PMID: 25193342 Free PMC article.
-
miR-21 and miR-145 cooperation in regulation of colon cancer stem cells.Mol Cancer. 2015 May 1;14:98. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0372-7. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25928322 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin: a potential therapeutic agent for recurrent colon cancer.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 20;9(1):e84369. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084369. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465408 Free PMC article.
-
Difluorinated Curcumin: A Promising Curcumin Analogue with Improved Anti-Tumor Activity and Pharmacokinetic Profile.Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(28):4386-97. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666160527113501. Curr Pharm Des. 2016. PMID: 27229723 Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
An overview of natural products that modulate the expression of non-coding RNAs involved in oxidative stress and inflammation-associated disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 24;14:1144836. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1144836. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37168992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Role of Curcumin as a Regulator of microRNA in Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review.Microrna. 2025;14(1):42-48. doi: 10.2174/0122115366304114240904051429. Microrna. 2025. PMID: 39279107
-
Cancer stem cells in colorectal cancer and the association with chemotherapy resistance.Med Oncol. 2021 Mar 18;38(4):43. doi: 10.1007/s12032-021-01488-9. Med Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33738588 Review.
-
Overexpression of miR-21-5p as a predictive marker for complete tumor regression to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer patients.BMC Med Genomics. 2014 Dec 11;7:68. doi: 10.1186/s12920-014-0068-7. BMC Med Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25496125 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mechanism of lncRNA and miRNA interaction: CCAT2 regulates miR-145 expression by suppressing its maturation process in colon cancer cells.Mol Cancer. 2017 Sep 30;16(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0725-5. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28964256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society, author. Colorectal Cancer Facts & Figures 2011–2013. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society Inc; 2011.
-
- Dean M, Fojo T, Bates S. Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:275–284. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
