Generation of gene-modified mice via Cas9/RNA-mediated gene targeting
- PMID: 23545779
- PMCID: PMC3641603
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2013.46
Generation of gene-modified mice via Cas9/RNA-mediated gene targeting
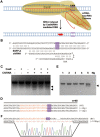
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

