Treating B-cell cancer with T cells expressing anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptors
- PMID: 23546520
- PMCID: PMC6322669
- DOI: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2013.46
Treating B-cell cancer with T cells expressing anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptors
Abstract
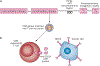
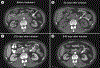
Most B-cell malignancies express CD19, and a majority of patients with B-cell malignancies are not cured by current standard therapies. Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) are fusion proteins consisting of antigen recognition moieties and T-cell activation domains. T cells can be genetically modified to express CARs, and adoptive transfer of anti-CD19 CAR T cells is now being tested in clinical trials. Effective clinical treatment with anti-CD19 CAR T cells was first reported in 2010 after a patient with advanced-stage lymphoma treated at the NCI experienced a partial remission of lymphoma and long-term eradication of normal B cells. Additional patients have subsequently obtained long-term remissions of advanced-stage B-cell malignancies after infusions of anti-CD19 CAR T cells. Long-term eradication of normal CD19(+) B cells from patients receiving infusions of anti-CD19 CAR T cells demonstrates the potent antigen-specific activity of these T cells. Some patients treated with anti-CD19 CAR T cells have experienced acute adverse effects, which were associated with increased levels of serum inflammatory cytokines. Although anti-CD19 CAR T cells are at an early stage of development, the potent antigen-specific activity observed in patients suggests that infusions of anti-CD19 CAR T cells might become a standard therapy for some B-cell malignancies.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
S. A. Rosenberg declares an association with the following company: Kite Pharma. See the article online for full details of the relationship. J. N. Kochenderfer declares no competing interests.
Figures
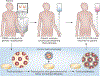
References
-
- National Cancer Institute. Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results [online], http://seer.cancer.gov/ (2013).
-
- Flowers CR & Armitage JO A decade of progress in lymphoma: Advances and continuing challenges. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 10, 414–423 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Sinha R, DeJoubner N & Flowers C Novel agents for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 20, 669–680 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Sehn LH et al. The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood 109, 1857–1861 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Kenkre VP & Smith SM Management of relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Curr. Oncol. Rep 10, 393–403 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

