Matrix metalloproteinase Mmp-1a is dispensable for normal growth and fertility in mice and promotes lung cancer progression by modulating inflammatory responses
- PMID: 23548910
- PMCID: PMC3656316
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.439893
Matrix metalloproteinase Mmp-1a is dispensable for normal growth and fertility in mice and promotes lung cancer progression by modulating inflammatory responses
Erratum in
-
Matrix metalloproteinase Mmp-1a is dispensable for normal growth and fertility in mice and promotes lung cancer progression by modulating inflammatory responses.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jul 27;293(30):11970. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AAC118.004704. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30054294 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
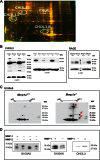
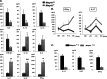
Human MMP-1 is a matrix metalloproteinase repeatedly associated with many pathological conditions, including cancer. Thus, MMP1 overexpression is a poor prognosis marker in a variety of advanced cancers, including colorectal, breast, and lung carcinomas. Moreover, MMP-1 plays a key role in the metastatic behavior of melanoma, breast, and prostate cancer cells. However, functional and mechanistic studies on the relevance of MMP-1 in cancer have been hampered by the absence of an in vivo model. In this work, we have generated mice deficient in Mmp1a, the murine ortholog of human MMP1. Mmp1a(-/-) mice are viable and fertile and do not exhibit obvious abnormalities, which has facilitated studies of cancer susceptibility. These studies have shown a decreased susceptibility to develop lung carcinomas induced by chemical carcinogens in Mmp1a(-/-) mice. Histopathological analysis indicated that tumors generated in Mmp1a(-/-) mice are smaller than those of wild-type mice, consistently with the idea that the absence of Mmp-1a hampers tumor progression. Proteomic analysis revealed decreased levels of chitinase-3-like 3 and accumulation of the receptor for advanced glycation end-products and its ligand S100A8 in lung samples from Mmp1a(-/-) mice compared with those from wild-type. These findings suggest that Mmp-1a could play a role in tumor progression by modulating the polarization of a Th1/Th2 inflammatory response to chemical carcinogens. On the basis of these results, we propose that Mmp1a knock-out mice provide an excellent in vivo model for the functional analysis of human MMP-1 in both physiological and pathological conditions.
Keywords: Carcinogenesis; Degradome; Inflammation; Invasion; Metastasis; Protease.
Figures



References
-
- Fanjul-Fernández M., Folgueras A. R., Cabrera S., López-Otín C. (2010) Matrix metalloproteinases: evolution, gene regulation and functional analysis in mouse models. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1803, 3–19 - PubMed
-
- Coussens L. M., Fingleton B., Matrisian L. M. (2002) Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and cancer: trials and tribulations. Science 295, 2387–2392 - PubMed
-
- Overall C. M., López-Otín C. (2002) Strategies for MMP inhibition in cancer: innovations for the post-trial era. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 657–672 - PubMed
-
- Egeblad M., Werb Z. (2002) New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 161–174 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

